ESP8266 with Telegram Messenger for Monitoring Temperature and Humidity using DHT11
Table of Contents
ESP8266 with Telegram Messenger:
ESP8266 with Telegram Messenger for Monitoring Temperature and Humidity using DHT11- So far, I have been using different IoT Platforms for monitoring different types of sensors and for controlling different types of electrical loads. The most popular IoT platforms that I have been using for quite a long time include the Blynk application, Arduino IoT Cloud, Ubidots, Thingspeak, and Firebase. Just like all these IoT platforms, you can also use Telegram Messenger as an IoT platform for monitoring sensors and for controlling electrical loads. This is my first article on Telegram Messenger and I will try my level best to explain each and every detail so that you can easily understand how to get started with Telegram Messenger. Since this is a getting started tutorial, that’s why I decided to start with the most basic sensor which is the DHT11 Temperature and Humidity Sensor. You can use Telegram Messenger with different controller boards which of course I will cover in my upcoming videos and articles, but for now, I will start with the Nodemcu ESP8266 WiFi Module. Before, I am going to share with you the test results, first, a few words about the sponsor of this project for helping me purchase the required components and tools.
Altium Designer:
Altium Designer is the world’s most trusted PCB design system. Altium Designer enables engineers to effortlessly connect with every facet of the electronics design process. Over 35 years of innovation and development focused on a truly unified design environment makes it the most widely used PCB design solution. With Altium Designer you can create PCB designs with an intuitive and powerful interface that connects you to every aspect of the electronics design process. Route it your way through any angle, tune for the delay, Push, Slide, and Walkaround faster than ever. Interact and collaborate with mechanical designers like never before in a photo-realistic, 3D design environment. If you want to get started with the Altium designer, you can click on the get started.
Telegram for Sensor Monitoring:
I powered up my Nodemcu ESP8266 WiFi module using a 12V power supply. I have this 7805 voltage regulator which converts 12 volts into regulated 5 volts. Next, I opened the Telegram Messenger and then I opened the Tempmonitoringbot.
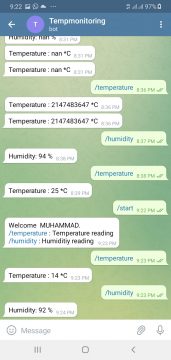
You can see the previously implemented commands, I have been testing it for a while and it’s working perfectly. You can request the temperature and humidity data from anywhere in the world, all you need is to write the command or simply click on the command and then wait for a few seconds, the reply time depends on the internet speed. In the same way, we can request the temperature value.
Isn’t it cool? You simply create a Bot in Telegram Messenger that hardly takes a minute and then this Bot takes care of all the communications. Anyways, you can see it’s working just perfectly. Now, it’s time to explain the circuit diagram and programming of this IoT-based project using Telegram Messenger, Nodemcu ESP8266, and DHT11 Temperature and Humidity Sensor. Without any further delay, let’s get started!!!
Amazon Links:
DHT11 Temperature and Humidity Module:
Other Tools and Components:
Super Starter kit for Beginners
PCB small portable drill machines
*Please Note: These are affiliate links. I may make a commission if you buy the components through these links. I would appreciate your support in this way!
ESP8266 (NodeMCU):
ESP8266 is a highly integrated chip designed for the needs of a new connected world. It offers a complete and self-contained Wi-Fi networking solution, allowing it to either host the application or to offload all Wi-Fi networking functions from another application processor.
ESP8266 has powerful on-board processing and storage capabilities that allow it to be integrated with the sensors and other application-specific devices through its GPIOs with minimal development up-front and minimal loading during runtime. Its high degree of on-chip integration allows for minimal external circuitry, and the entire solution, including front-end module, is designed to occupy minimal PCB area.
Specifications:
Serial/UART baud rate: 115200 bps
Input power: 3.3V
I/O voltage tolerance: 3.6V Max
Flash Memory Size: 1MB (8Mbit)
WiFi security modes: WPA, WPA2
DHT 11 Sensor:
- DHT11 digital temperature and humidity sensor is a digital signal output with a calibrated temperature and humidity combined sensor.
- It uses a dedicated digital modules and acquisition of temperature and humidity sensor technology to ensure that products with high reliability and excellent long term stability.
- Sensor consists of a resistive element and a sense of wet NTC temperature measurement devices, and with a high-performance 8-bit microcontroller connected.
- The product has excellent quality, fast response, anti-interference ability, high cost and other advantages.
- The single-wire wiring scheme makes it easy to be integrated to other applications and the simple communication protocol greatly reduces the programming effort required.
Nodemcu ESP8266 with DHT11 Circuit Diagram:
Connect pin number1 of the DHT11 sensor with the 3.3V pin of the Nodemcu ESP8266. Connect pin number2 which is the data pin with the D1 pin of the Nodemcu ESP8266. Pin number3 is not connected. Finally, connect pin number4 of the DHT11 sensor with the GND pin of the Nodemcu ESP8266 WiFi Module. These are the minimum connections which you can start with, you can use your laptop or computer to power up the Nodemcu ESP8266. But if you want to practically implement this then you will need to add an external power supply; I have a very detailed video on this, I will provide a link in the description. Now, let’s start the interfacing.
- Connect the middle pin which is signal pin of the DHT11 with the D1 of the ESP8266.
- Connect the ground of the DHT11 with the ground of the ESP8266.
- Connect the VCC of the DHT11 with the 3V of the ESP8266.
Connect the data pin with the D1 pin.
Connect the VCC pin with 3.3V pin.
Finally, connect the GND pin of the DHT11 Sensor with the GND pin of the Nodemcu ESP8266. Our interfacing is completed.
Creating Telegram Bot:
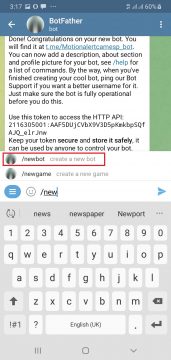
First of all download the telegram app from the play store which is available free of cost. Then open the telegram app and in the search write botfather with the help of which we will design the app.
Then we will create the new Bot for our application for which we will write /newbot
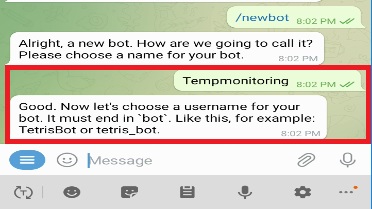
When we will write this command we will receive the message that choose the name for your bot
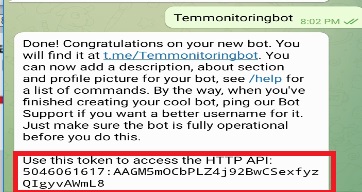
Next, we will choose the username, we can select any name but it must end in bot. Our Bot is created and we can use this token to access the HTTP API, we will use this in the Nodemcu ESP8266 programming.
Nodemcu ESP8266 Board Manager Installation:
If this is your first time using the Nodemcu ESP8266 WiFi module, then first of all, you will need to install the Nodemcu board, as you can see the Nodemcu board is not installed.
To install the Nodemcu board click on the file menu and then click on the preferences.
Then in the preference paste the following link
|
1 |
https://dl.espressif.com/dl/package_esp32_index.json, http://arduino.esp8266.com/stable/package_esp8266com_index.json |
As we are going to install both ESP32 and E8266 board setup so will paste both links separated by comma and click on ok. If you want to install the esp8266 only then copy the second link.
After that we will again open the board manager for which we will click on the tools and then select the board manager.
Click on the board manager. Type ESP8266 in the search box, select the latest version and then click on the install button. This may take several minutes depending on the internet speed. Click on the Close button when the installation is completed.
Then we will select the NodeMCU
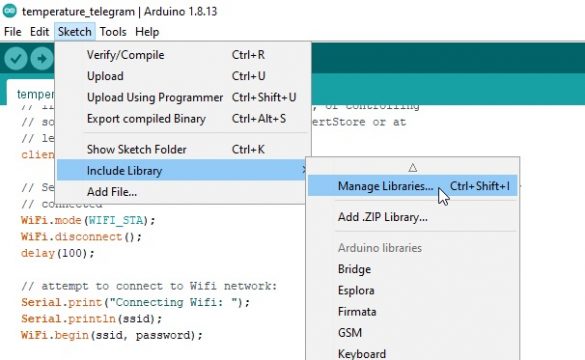
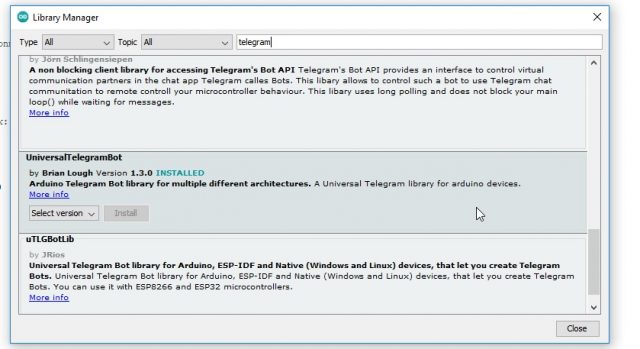
After installing the NodeMCU board we will install the library for the telegram app for which we will go to the sketch, then click on the include library and then click on the manage library.
In the library manager we will write the telegram and install the UniversalTelegramBot library. I have already installed this library.
Telegram Nodemcu ESP8266 Programming:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 |
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h> #include <WiFiClientSecure.h> #include <UniversalTelegramBot.h> #include "DHT.h" #define DHTPIN D1 #define DHTTYPE DHT11 // DHT 11 DHT dht(DHTPIN, DHTTYPE); // Initialize Wifi connection to the router char ssid[] = "AndroidAP3DEC"; // Wifi Name char password[] = "123456"; // Wifi Password // Initialize Telegram BOT #define BOTtoken "5046061617:AAGM5mOCbPLZ4j92BwCSexfyzQIgyvAWmL8" // Bot token from telegram app WiFiClientSecure client; UniversalTelegramBot bot(BOTtoken, client); //Checks for new messages every 1 second. int botRequestDelay = 1000; unsigned long lastTimeBotRan; void handleNewMessages(int numNewMessages) { Serial.println("handleNewMessages"); Serial.println(String(numNewMessages)); for (int i=0; i<numNewMessages; i++) { String chat_id = String(bot.messages[i].chat_id); String text = bot.messages[i].text; String from_name = bot.messages[i].from_name; if (from_name == "") from_name = "Guest"; if (text == "/temperature") { int t = dht.readTemperature(); String temp = "Temperature : "; temp += int(t); temp +=" *C\n"; bot.sendMessage(chat_id,temp, ""); } if (text == "/humidity") { int h = dht.readHumidity(); String temp = "Humidity: "; temp += int(h); temp += " %"; bot.sendMessage(chat_id,temp, ""); } if (text == "/start") { String welcome = "Welcome " + from_name + ".\n"; welcome += "/temperature : Temperature reading\n"; welcome += "/humidity : Humiditiy reading\n"; bot.sendMessage(chat_id, welcome, "Markdown"); } } } void setup() { Serial.begin(115200); dht.begin(); // This is the simplest way of getting this working // if you are passing sensitive information, or controlling // something important, please either use certStore or at // least client.setFingerPrint client.setInsecure(); // Set WiFi to station mode and disconnect from an AP if it was Previously // connected WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA); WiFi.disconnect(); delay(100); // attempt to connect to Wifi network: Serial.print("Connecting Wifi: "); Serial.println(ssid); WiFi.begin(ssid, password); while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) { Serial.print("."); delay(500); } Serial.println(""); Serial.println("WiFi connected"); Serial.print("IP address: "); Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); } void loop() { int t = dht.readTemperature(); int h = dht.readHumidity(); if (millis() > lastTimeBotRan + botRequestDelay) { int numNewMessages = bot.getUpdates(bot.last_message_received + 1); while(numNewMessages) { Serial.println("got response"); handleNewMessages(numNewMessages); numNewMessages = bot.getUpdates(bot.last_message_received + 1); } lastTimeBotRan = millis(); } } |
Telegram Nodemcu ESP8266 Code Explanation:
First of all we will add the libraries for the Nodemcu, Telegram, and DHT11 sensor.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h> #include <WiFiClientSecure.h> #include <UniversalTelegramBot.h> #include "DHT.h" |
Next, I defined a pin to which the Dht11 sensor is connected, in my case D1.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
#define DHTPIN D1 #define DHTTYPE DHT11 // DHT 11 DHT dht(DHTPIN, DHTTYPE); |
Then we will write the WiFi name and password.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
// Initialize Wifi connection to the router charssid[] = "AndroidAP3DEC"; // Wifi Name char password[] = "123456"; // Wifi Password |
Here we will paste the command bot token which we have copied during the telegram bot creation.
|
1 2 3 |
// Initialize Telegram BOT #define BOTtoken "5046061617:AAGM5mOCbPLZ4j92BwCSexfyzQIgyvAWmL8" // Bot token from telegram app |
Now with WifiClientSecure create Wifi client
|
1 |
WiFiClientSecure client; |
Now create a bot from the client and bot token
|
1 |
UniversalTelegramBotbot(BOTtoken, client); |
Checks for new messages every 1 second.
|
1 2 3 |
intbotRequestDelay = 1000; unsigned long lastTimeBotRan; |
This function will handle the message which will be received from the telegram application
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
voidhandleNewMessages(intnumNewMessages) { Serial.println("handleNewMessages"); Serial.println(String(numNewMessages)); for (int i=0; i<numNewMessages; i++) { String chat_id = String(bot.messages[i].chat_id); String text = bot.messages[i].text; String from_name = bot.messages[i].from_name; if (from_name == "") from_name = "Guest"; |
Now if the message received from the telegram temperature then it will send temperature to the telegram application.
|
1 2 3 |
//CekPembacaan Sensor DHT11 if (text == "/temperature") { |
This command will store the current value of the temperature
|
1 |
int t = dht.readTemperature(); |
Then we have declare temp of string variable type in which we will save the temperature and its value and send it to the telegram.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
String temp = "Temperature : "; temp += int(t); temp +=" *C\n" bot.sendMessage(chat_id,temp, ""); } |
If we receive humidity message from the telegram application then it will read the humidity and send it to the telegram.
|
1 |
if (text == "/humidity") { |
This command will read the humidity and store it in the variable then we have declare string variable which will store the text humidity and its value in percentage and send it to the telegram application.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
int h = dht.readHumidity(); String temp = "Humidity: "; temp += int(h); temp += " %"; bot.sendMessage(chat_id,temp, ""); } |
Now if we receive the message start from the user then it will display temperature and humidity.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
if (text == "/start") { String welcome = "Welcome " + from_name + ".\n"; welcome += "/temperature : Temperature reading\n"; welcome += "/humidity : Humiditiy reading\n"; bot.sendMessage(chat_id, welcome, "Markdown"); } } } void setup() { |
In the setup function we will start the serial communication of the DHT sensor and connect the Wifi with the router.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 |
Serial.begin(115200); dht.begin(); // This is the simplest way of getting this working // if you are passing sensitive information, or controlling // something important, please either use certStore or at // least client.setFingerPrint client.setInsecure(); // Set WiFi to station mode and disconnect from an AP if it was Previously // connected WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA); WiFi.disconnect(); delay(100); // attempt to connect to Wifi network: Serial.print("Connecting Wifi: "); Serial.println(ssid); WiFi.begin(ssid, password); while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) { Serial.print("."); delay(500); } Serial.println(""); Serial.println("WiFi connected"); Serial.print("IP address: "); Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); } void loop() { |
Here we will get the temperature and humidity values from the sensor.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
int t = dht.readTemperature(); int h = dht.readHumidity(); if (millis() >lastTimeBotRan + botRequestDelay) { intnumNewMessages = bot.getUpdates(bot.last_message_received + 1); while(numNewMessages) { Serial.println("got response"); handleNewMessages(numNewMessages); numNewMessages = bot.getUpdates(bot.last_message_received + 1); } lastTimeBotRan = millis(); } } |
After uploading code to the NodeMCU ESP8266 we will open the telegram application and open the temp monitoring chat. When we will write /start in it we will get the message /temperature and /humidity. If we click or write /temperature then we will get the temperature and if we click or wrtie the /humidity then we will get the percentage of humidity.
Watch Tutorial:










How do I manage to get from the “Token” message to the next step to select the ESP board ? How to activate this window ?
Dear Shahzada Fahad,
In your project ESP8266 with Telegram Messenger for Monitoring Temperature and Humidity using DHT11,
I would like to replace the DHT11 for a humidity soil sensor model M-SENS-V1.2
I would like that Telegram Bot advice me for a threshold of humidity, fixed in the sketch, and maybe give me historical readings as requests.
I would great appreciated if you can help me with conections and code.
I am novice and have a very little experince in programing.
Thank you for your help, and have good time,
Ramon