A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Sensor with Arduino, ESP32, & ESP8266
Table of Contents
A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Sensor:
A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Sensor with Arduino, ESP32, & ESP8266- today we are going to use A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Sensor with Arduino, ESP32 WiFi + Bluetooth Module, and the Nodemcu ESP8266 WiFi module.
I’ve already written quite detailed articles on the HC-SR04 and JSN SR04T Waterproof Ultrasonic sensors. I’ve used both of these sensors in projects ranging from beginners to intermediate and advanced levels. So, in this article, I won’t go into much detail about these sensors; I’ll just do a brief comparison. But if you want to know more about these sensors in detail, you can check out my previous videos and articles.
Anyway, let’s do a side by side comparison of the A02YYUM Waterproof Ultrasonic Sensor with its ultrasonic siblings.
| A02YYUW | HC-SR04 | JSN SR04T |
| Waterproof: Yes
Operating Voltage: 3.3~5V standby Current: ≤5mA Working Current: ≤8mA Blind Zone Distance: 3cm Ranging Distance: 3-450cm Output: UART Response Time: 100ms Frequency: 40kHz Operating Temperature: -15~60℃ Sensing Angle: 60° Protection Rate: IP67 |
Waterproof: No
Operating Voltage: 5V standby Current: ≤2mA Working Current: ≤15mA Blind Zone Distance: 2cm Ranging Distance: 2-400cm Output: TTL Response Time: 20ms Frequency: 40kHz Operating Temperature: -15~70℃ Sensing Angle: 15° Cone Protection Rate: No |
Waterproof: Yes Operating Voltage: 5V standby Current: ≤5mA Working Current: ≤30mA Blind Zone Distance: 25cm Ranging Distance: 25-450cm Output: TTL and UART Response Time: 65ms Frequency: 40kHz Operating Temperature: -10~70℃ Sensing Angle: <50° Protection Rate: only the sensor |
Waterproof:
The A02YYUW Ultrasonic Sensor is waterproofed and its protection rate is IP67; the entire sensor is protected against dust and water.
Whereas the HC-SR04 is not designed to be waterproof or weather-resistant. It does not have a specific protection rate against dust or water. It is recommend to use the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor in environment where it won’t be exposed to moisture or harsh weather conditions.
While the JSN SR04T is designed to be waterproof and has a protection rate against dust and water. This makes the JSN SR04T suitable for applications where water resistance is necessary, such as outdoor projects or environments where the sensor might be exposed to rain or moisture. It should be noted, only the sensor part is waterproofed and not the interface board. So, make sure you keep the circuit part in a waterproof enclosure.
Operating Voltage:
The Operating voltage of the A02YYUW waterproof Ultrasonic Sensor is from 3.3V to 5V DC. So, its compatible with ESP32, ESP8266, STM32, Raspberry Pi Pico etc which are 3.3V compatible controller boards and also with Arduino, Raspberry Pi etc which are 5V compatible controller boards.
Whereas the HC-SR04 and JSN SR04T ultrasonic sensors are 5V compatible controller boards. You can safely use it with Arduino and Raspberry Pi but if you are planning on using these sensors with 3.3V compatible controller boards then you will have to use voltage converters.
Working Current:
The working current of A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic sensor is 8mA.
The working current of HC-SR04 Ultrasonic sensor is 15mA. And
The Working current of JSN SR04T Waterproof Ultrasonic Sensor is 30mA.
The exact working current of the Ultrasonic Sensor can vary slightly based on factors like operating conditions and specifications of the particular model.
Blind Zone Distance:
The Blind Zone Distance of the A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic sensor is 3cm; it means that the sensor may not reliably detect objects that are closer than 3cm. The blind zone distance of an ultrasonic sensor refers to the minimum distance within which the sensor is unable to provide accurate distance measurements.
The Blind zone distance of the HC-SR04 is 2cm. Whereas the Blind zone distance of the JSN SR04T is 25cm.
A02YYUW falls in between HC-SR04 and JSN SR04T in terms of blind zone distance. It offers a compromise between close-range precision and longer-range performance.
Ranging Distance:
The A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic sensor has a ranging distance of 3-450cm.
The HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor has a ranging distance of 2-400cm. And
The JSN SR04T Waterproof Ultrasonic Sensor has a ranging distance of 25-450cm.
Output:
The output of the A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic sensor is UART.
The output of the HC-SR04 is TTL. And
The output of the JSN SR04T is TTL and UART.
Response Time:
Response time of the A02YYUW is 100ms.
Response time of the HC-SR04 is 20ms. And
Response time of the JSN SR04T is 65ms.
The exact response time may vary slightly depending on factors such as the specific model, environmental conditions, and the microcontroller or system it is connected to.
Frequency:
All the three Ultrasonic sensors are 40kHz.
Operating Temperature:
The operating temperature of the A02YYUW is between -15~60℃.
The Operating temperature of the HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor is between -15~70℃. And
The operating temperature of the JSN SR04T Ultrasonic Sensor is between -10~70℃.
Keep in mind that these are general specifications, and the actual performance in extreme temperatures may vary. If you have specific temperature requirements for your application, it’s advisable to refer to the datasheet or technical specifications provided by the manufacturer for the precise details related to the model you are using.
Sensing Angle:
The sensing angle of A02YYUM Waterproof Ultrasonic sensor is 60°.
The Sensing angle of the HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor is 15° Cone shaped. And
The Sensing angle of the JSN SR04T Waterproof Ultrasonic sensor is less then 50°.
The sensing angle is a crucial factor to consider when positioning the sensor in a project, as it determines the coverage area and influences the sensor’s effectiveness in detecting objects within its field of view. A wider sensing angle might be beneficial in applications where a larger detection area is required.
After this detailed comparison, now you have an idea that the A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Sensor is better in every aspect, especially its voltage range, maximum distance range, sensing angle, accuracy, and protection rating.
Now, we are going to use this Ultrasonic Sensor with Arduino, Nodemcu ESP8266 WiFi module, and ESP32 WiFi + Bluetooth Module. So, without any further delay, let’s get started!!!
Amazon Links:
Arduino Nano USB-C Type (Recommended)
A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic sensor
ESP32 WiFi + Bluetooth Module(Recommended)
Other Tools and Components:
Super Starter kit for Beginners
PCB small portable drill machines
*Please Note: These are affiliate links. I may make a commission if you buy the components through these links. I would appreciate your support in this way!
As usual, I am using my designed Arduino Nano development board, but you can also use Arduino Uno.
Required Libraries:
Before, you start the programming; first of all, make sure you install these libraries.
Adafruit_SSD1306
Adafruit_GFX
Simply, copy the library name, then go to the Sketch Menu, then to Include Library, and Click on the manage libraries.
Paste the library name in the search box and install the library. As you can see I have already installed this library.
Now, follow the same exact steps for the other library.
A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Sensor with Arduino:
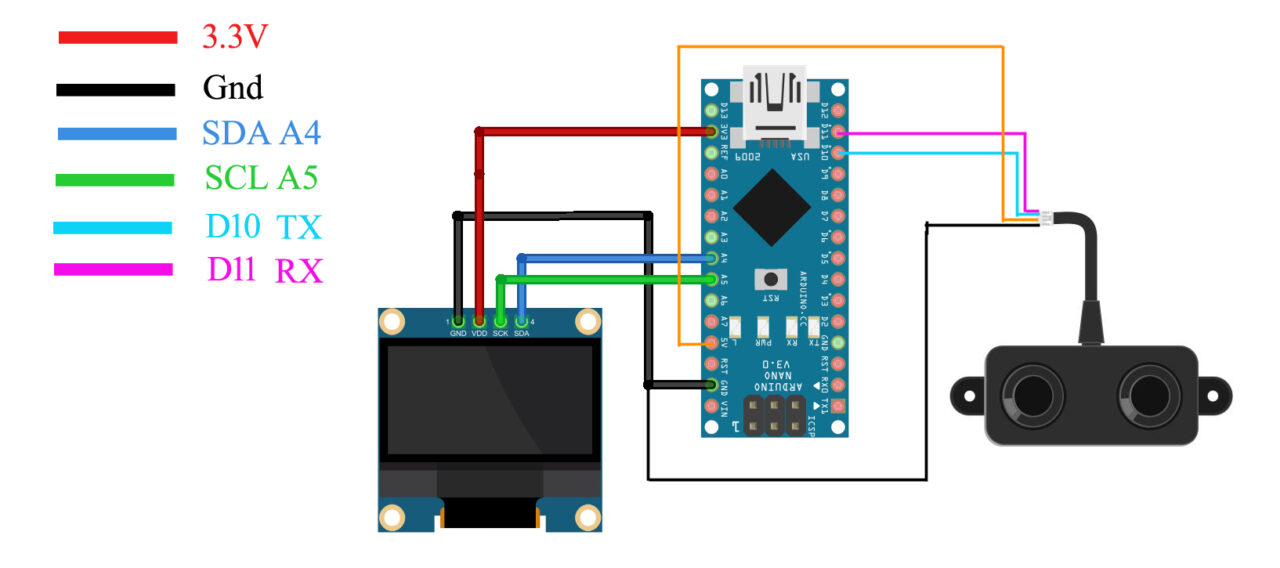
Connect the VCC and GND wires of the A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Sensor to the Arduino 5V and GND pins. Connect the Tx and Rx pins of the Ultrasonic Sensor to the Arduino D10 and D11 pins.
Connect the VCC and GND pins of the SSD1306 Oled display module to the Arduino 3.3V and GND pins. Connect the SDA and SCL pins of the Oled display module to the Arduino A4 and A5 pins. A4 is the SDA and A5 is the SCL. And now let’s go ahead and take at the programming.
A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Sensor with Arduino Programming:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 |
#include <Wire.h> #include <Adafruit_GFX.h> #include <Adafruit_SSD1306.h> #include <SoftwareSerial.h> SoftwareSerial mySerial(11,10); // RX, TX // connect yellow wire to D10 and White wire to D11 unsigned char data[4]={}; float distance; #define SCREEN_WIDTH 128 // OLED display width, in pixels #define SCREEN_HEIGHT 64 // OLED display height, in pixels // Declaration for an SSD1306 display connected to I2C (SDA, SCL pins) #define OLED_RESET -1 // Reset pin # (or -1 if sharing Arduino reset pin) Adafruit_SSD1306 display(SCREEN_WIDTH, SCREEN_HEIGHT, &Wire, OLED_RESET); void setup() { Serial.begin(115200); mySerial.begin(9600); display.begin(SSD1306_SWITCHCAPVCC, 0x3C); delay(2000); display.clearDisplay(); display.setTextColor(WHITE); delay(1000); } void loop() { do{ for(int i=0;i<4;i++) { data[i]=mySerial.read(); } }while(mySerial.read()==0xff); mySerial.flush(); if(data[0]==0xff) { int sum; sum=(data[0]+data[1]+data[2])&0x00FF; if(sum==data[3]) { distance=(data[1]<<8)+data[2]; distance=distance / 10; Serial.println(distance); display.clearDisplay(); display.setCursor(10,0); display.setTextSize(2); display.setTextColor(WHITE); display.print("Distance"); display.setCursor(10,30); display.setTextSize(2); display.print(String(distance)+" cm"); display.display(); } } delay(100); } |
The advantage of using softwareSerial library is that I can define multiple serial ports, this way, I can use the Arduino default serial port of the debugging purposes. So, you can see, I have defined another serial port with the name mySerial. So, through this serial port I am going to communicate with the Ultrasonic Sensor.
This code is needed for the SSD1306 Oled display module, I have already explained it in my Arduino full course video. Anyway, the code is pretty straightforward, we simply read the A02YYUW waterproof ultrasonic sensor and then print the value on the Oled display module.
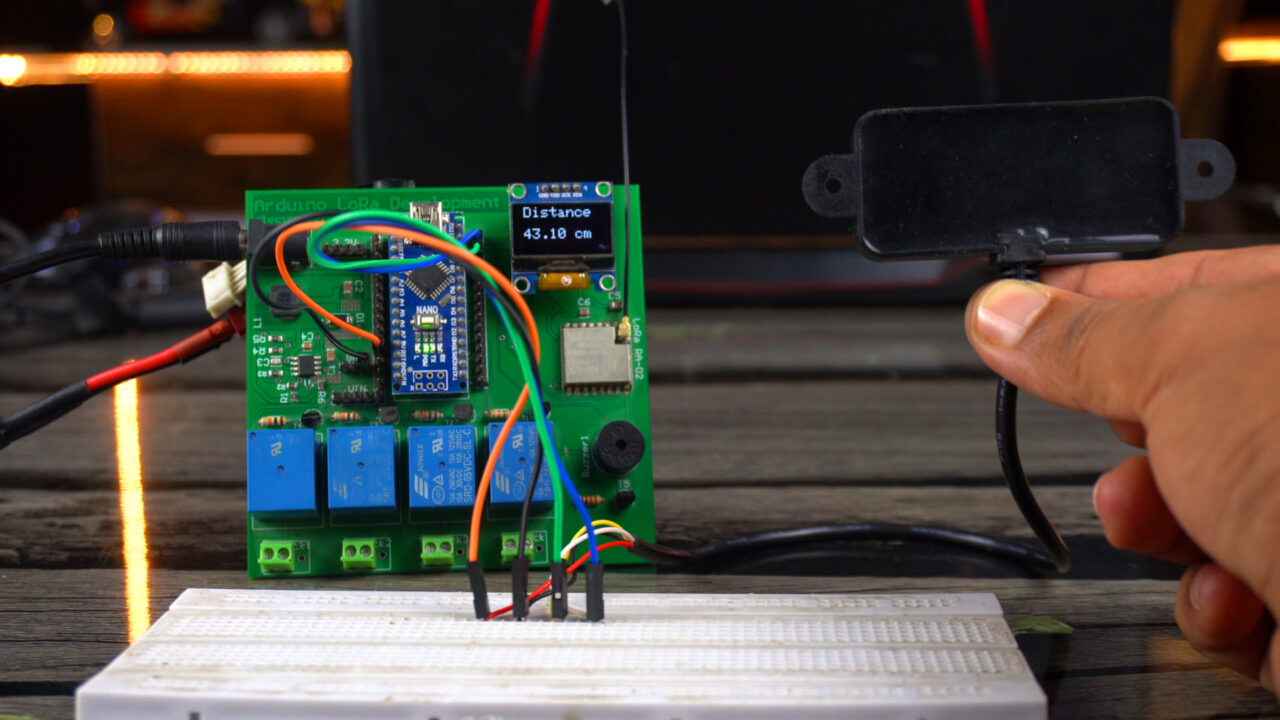
I have already uploaded this program and now let’s watch the Arduino and A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Sensor in Action.
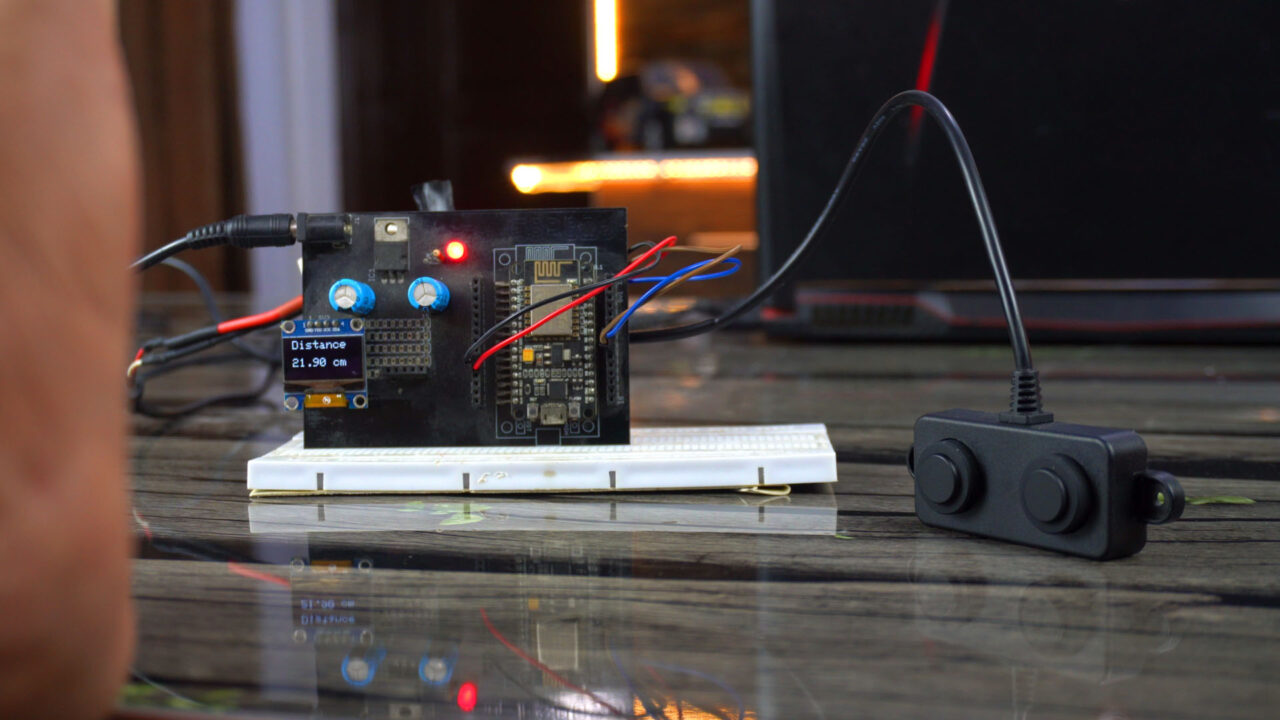
Practical Demonstration:
We just built a simple yet highly accurate distance meter. You can modify this project and covert it into a security system by adding some if conditions; so when an object or a human or anything else is detected by this sensor a buzzer will be turned ON. Or you can use this as an obstacle detector in a robot and this way you can control the motors. You can also use this as a water level sensor. There are countless ways you can use this sensor. It totally depends on your idea, how you decide to use it.
Next, we are going to use this Waterproof Ultrasonic Sensor with the Nodemcu ESP8266 WiFi Module.
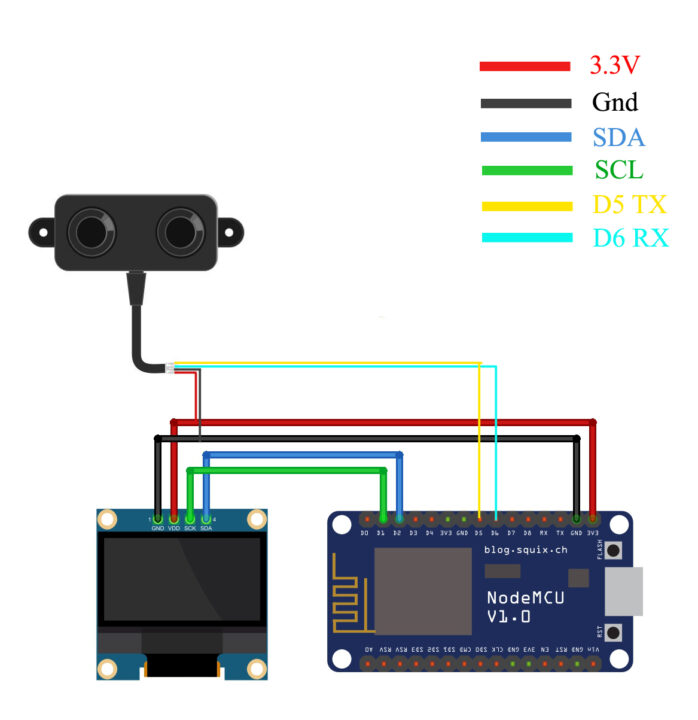
A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Sensor with ESP8266:
Connect the VCC and GND wires of the A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Sensor to the Nodemcu ESP8266 WiFi Module 3.3V and GND pins. Connect the Tx and Rx pins of the Ultrasonic Sensor to the ESP8266 D5 and D6 pins.
Connect the VCC and GND pins of the SSD1306 Oled display module to the Nodemcu ESP8266 WiFi Module 3.3V and GND pins. Connect the SDA and SCL pins of the Oled display module to the Nodemcu D2 and D1 pins. And now let’s go ahead and take at the programming.
A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Sensor with ESP8266 Programming:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 |
#include <Wire.h> #include <Adafruit_GFX.h> #include <Adafruit_SSD1306.h> #include <SoftwareSerial.h> SoftwareSerial mySerial(D6,D5); // RX, TX // connect yellow wire to D5 and White wire to D6 unsigned char data[4]={}; float distance; #define SCREEN_WIDTH 128 // OLED display width, in pixels #define SCREEN_HEIGHT 64 // OLED display height, in pixels // Declaration for an SSD1306 display connected to I2C (SDA, SCL pins) #define OLED_RESET -1 // Reset pin # (or -1 if sharing Arduino reset pin) Adafruit_SSD1306 display(SCREEN_WIDTH, SCREEN_HEIGHT, &Wire, OLED_RESET); void setup() { Serial.begin(115200); mySerial.begin(9600); display.begin(SSD1306_SWITCHCAPVCC, 0x3C); delay(2000); display.clearDisplay(); display.setTextColor(WHITE); delay(1000); } void loop() { do{ for(int i=0;i<4;i++) { data[i]=mySerial.read(); } }while(mySerial.read()==0xff); mySerial.flush(); if(data[0]==0xff) { int sum; sum=(data[0]+data[1]+data[2])&0x00FF; if(sum==data[3]) { distance=(data[1]<<8)+data[2]; distance=distance / 10; Serial.println(distance); display.clearDisplay(); display.setCursor(10,0); display.setTextSize(2); display.setTextColor(WHITE); display.print("Distance"); display.setCursor(10,30); display.setTextSize(2); display.print(String(distance)+" cm"); display.display(); } } delay(100); } |
This is the same exact program, this time I only changed the pins my ultrasonic sensor is connected to. While everything else remains exactly the same. And one more thing that I would like to talk about is, if this is your first time using the nodemcu ESP8266 WiFi module then you will need to install the ESP8266 Board in the Arduino IDE and for this you can read my getting started article on the Nodemcu ESP8266 WiFi module. In this article, I have explained how to add the board manager url link in the Arduino IDE and how to install different variants of the ESP8266.
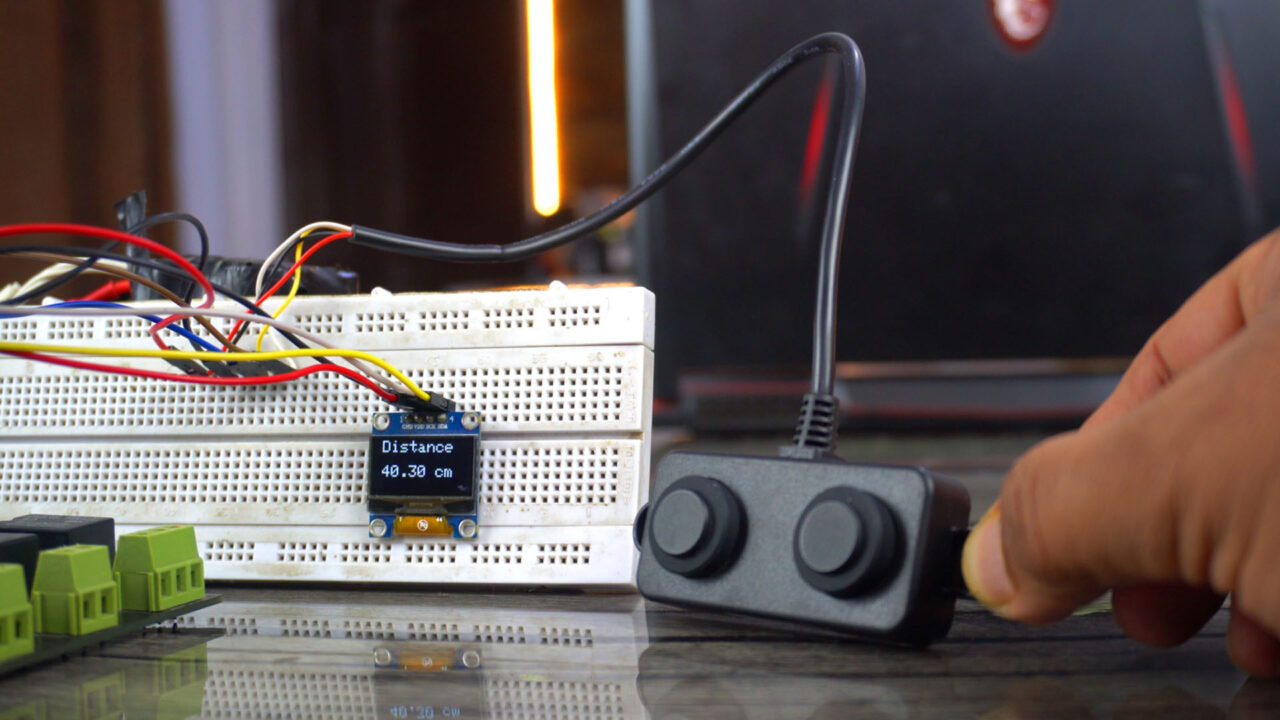
Anyway, I have already uploaded this program, and now let’s watch the A02YYUW waterproof ultrasonic sensor and Nodemcu ESP8266 WiFi module in action.
Next time, I will use this with Blynk application, so consider subscribing if you don’t want to miss any of my upcoming videos and articles.
Next, we are going to use this Ultrasonic Sensor with the ESP32 WiFi + Bluetooth module.
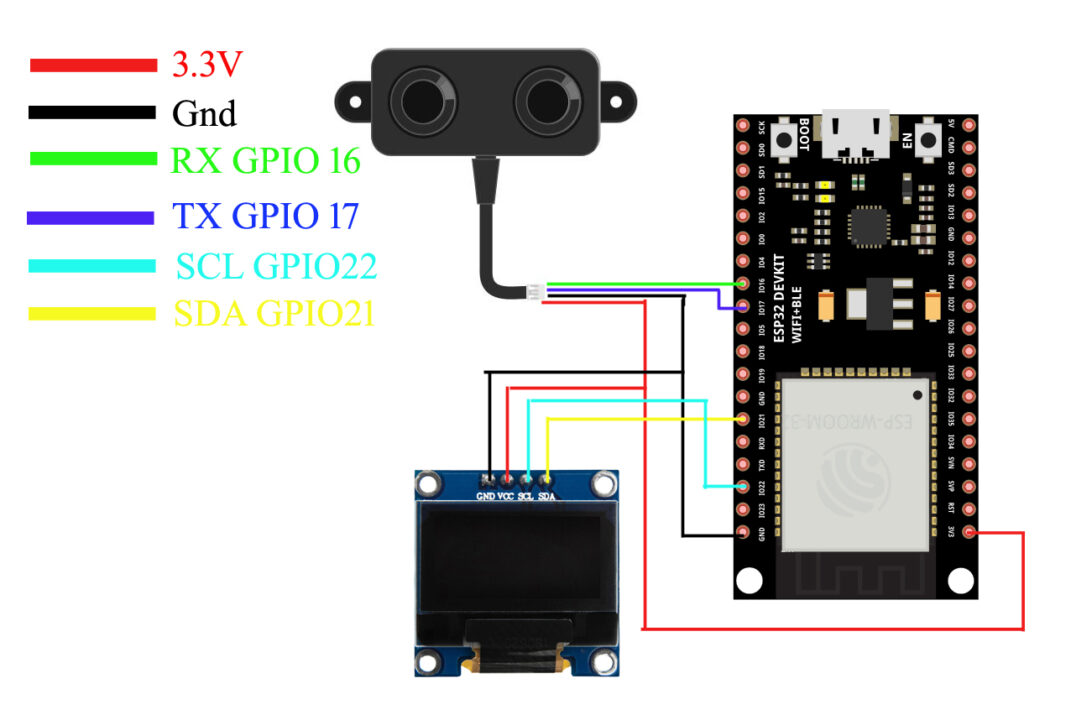
A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Sensor with ESP32:
Connect the VCC and GND wires of the A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Sensor to the ESP32 3.3V and GND pins. Connect the Tx and Rx pins of the Ultrasonic Sensor to the ESP32 GPIO16 and GPIO17.
Connect the VCC and GND pins of the SSD1306 Oled display module to the ESP32 3.3V and GND pins. Connect the SDA and SCL pins of the Oled display module to the ESP32 GPIO pins 21 and 22. And now let’s go ahead and take a look at the programming.
A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Sensor with ESP32 Programming:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 |
#include <Wire.h> #include <Adafruit_GFX.h> #include <Adafruit_SSD1306.h> #include <HardwareSerial.h> HardwareSerial Ultrasonic_Sensor(2); // TX2 (pin 17), RX2 (pin 16) unsigned char data[4] = {}; float distance; #define SCREEN_WIDTH 128 // OLED display width, in pixels #define SCREEN_HEIGHT 64 // OLED display height, in pixels // Declaration for an SSD1306 display connected to I2C (SDA, SCL pins) #define OLED_RESET -1 // Reset pin # (or -1 if sharing Arduino reset pin) Adafruit_SSD1306 display(SCREEN_WIDTH, SCREEN_HEIGHT, &Wire, OLED_RESET); void setup() { Serial.begin(115200); // Initialize the serial monitor Ultrasonic_Sensor.begin(9600); // Initialize the hardware serial display.begin(SSD1306_SWITCHCAPVCC, 0x3C); delay(2000); display.clearDisplay(); display.setTextColor(WHITE); delay(1000); } void loop() { do { for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { data[i] = Ultrasonic_Sensor.read(); } } while (Ultrasonic_Sensor.read() == 0xff); Ultrasonic_Sensor.flush(); if (data[0] == 0xff) { int sum; sum = (data[0] + data[1] + data[2]) & 0x00FF; if (sum == data[3]) { distance = (data[1] << 8) + data[2]; Serial.print("distance="); distance=distance / 10; Serial.println(distance); display.clearDisplay(); display.setCursor(10,0); display.setTextSize(2); display.setTextColor(WHITE); display.print("Distance"); display.setCursor(10,30); display.setTextSize(2); display.print(String(distance)+" cm"); display.display(); } } delay(100); } |
Again I am using the same exact libraries and code, but this time instead of using the softwareSerial library, I am using the HardwareSerial library. As ESP32 has got multiple serial ports. So, you can see, my waterproof ultrasonic sensor is connected to the Serial Port 2, and everything else remains exactly the same.
And let me also tell you, if this is your first time using the ESP32 WiFi + Bluetooth module then first of all, you will need to install the ESP32 board in the Arduino IDE and for this you can read my getting started article on the ESP32 WiFi + Bluetooth module.
Anyway, I have already, uploaded this program and now let’s watch the A02YYUW Waterproof Ultrasonic Sensor and ESP32 WiFi + Bluetooth module in action.