Math Object in JavaScript with Examples
Table of Contents
Math object:
Math Object in JavaScript– The math object is a JavaScript object. It consists of properties (or constants) and methods. All these properties and method can be called by using directly math object. Mostly its methods are used to perform different mathematical tasks.
Amazon Purchase Links:
*Please Note: These are affiliate links. I may make a commission if you buy the components through these links. I would appreciate your support in this way!
Methods of math JavaScript object:
The most crucial and commonly used methods of math object are as follows:
Abs():
This method returns the absolute value of a give number. The general syntax to use this method is:
Math.abs(number);
For example
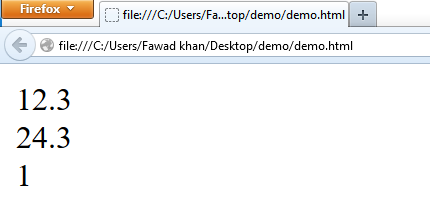
12.3 returns 12.3
-24.3 returns 24.3
3-2 returns 1
The following code demonstrates the function of Math.abs():
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
<html> <head> <script type="text/javaScript"> var a=12.3; var b= -24.3; var c=3-2; document.write(Math.abs(a)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.abs(b)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.abs(c)+"<br>"); </script> </head> <body> </body> </html> |
Sqrt():
This method returns the square root of a given positive number. This method returns NaN if the given number is negative. The general syntax to use this method is:
Math.sqrt(number);
For example:
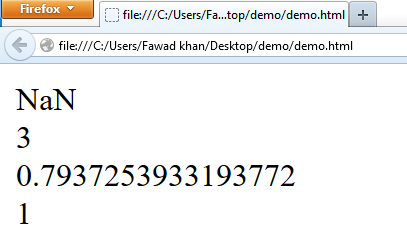
Math.sqrt(-4) returns NaN.
Math.sqrt(9) returns 3.
Math.sqrt(0.64) returns 0.7937.
Math.sqrt(1) returns 1.
The following code demonstrates the function of Math.sqrt():
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
<html> <head> <script type="text/javaScript"> var a=-4; var b= 9; var c=0.63; var d= 1; document.write(Math.sqrt(a)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.sqrt(b)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.sqrt(c)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.sqrt(d)+"<br>"); </script> </head> <body> </body> </html> |
Ceil():
This method returns the value of a given number rounded upwards to the nearest integer. The general syntax to use this method is:
Math.ceil(number);
Example:
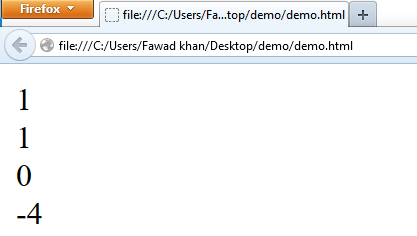
Math.ceil(0.65) returns 1.
Math.ceil(0.40) returns 1.
Math.ceil(6.1) returns 7.
Math.ceil(-6.9) returns -6.
Math.ceil(-6.1) returns -6.
The following code demonstrates the function of Math.ceil():
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
<html> <head> <script type="text/javaScript"> var a=0.65; var b= 0.40; var c=6.1; var d= -6.9; var e= -6.1; document.write(Math.ceil(a)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.ceil(b)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.ceil(c)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.ceil(d)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.ceil(e)+"<br>"); </script> </head> <body> </body> </html> |
Floor():
This method returns the value of a given number rounded downwards to the nearest integer. The general syntax to use this method is:
Math.floor(number);
Example:
Math.floor(0.65) returns 0.
Math.floor(0.40) returns 0.
Math.floor(6.1) returns 6.
Math.floor(-6.9) returns -7.
Math.floor(-6.1) returns -7.
The following code demonstrates the function of Math.floor():
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
<html> <head> <script type="text/javaScript"> var a=0.65; var b= 0.40; var c=6.1; var d= -6.9; var e= -6.1; document.write(Math.floor(a)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.floor(b)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.floor(c)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.floor(d)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.floor(e)+"<br>"); </script> </head> <body> </body> </html> |
Pow():
This method is used to find the exponential power of a given number. The general syntax to use this method is:
Math.pow(x,y)
It returns the value of x to the power y ( xy).
Example:
Math.pow(2,2) returns 4.
Math.pow(3,2) returns 9.
Math.pow(-2,3) returns -8.
The following code demonstrates the function of Math.pow():
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
<html> <head> <script type="text/javaScript"> document.write(Math.pow(2,2)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.pow(3,2)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.pow(-2,3)+"<br>"); </script> </head> <body> </body> </html> |
Round():
This method rounds a number to the nearest integer. The general syntax to use this method is:
Math.round(number);
Example:
Math.round(0.51) returns 1.
Math.round(0.50) returns 1.
Math.round(0.49) returns 0.
Math.round(-3.55) returns -4.
The following code demonstrates the function of Math.round():
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
<html> <head> <script type="text/javaScript"> document.write(Math.round(0.51)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.round(0.50)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.round(0.49)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.round(-3.55)+"<br>"); </script> </head> <body> </body> </html> |
Random():
This method returns a random number between 0 and 1. The general syntax to use this method is:
Math.random();
To return a random number up to a specified number, multiply the number with this function. For example, to return a random number up to 1000, the statement is written as;
document.write(Math.random()*1000);
The following code demonstrates the function of Math.random():
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
<html> <head> <script type="text/javaScript"> document.write(Math.random()*1000+"<br>"); </script> </head> <body> </body> </html> |
max(x,y):
this method is used to find the maximum number of two numbers. The general syntax to use this method is:
Math.max(x,y);
Example:
Math.max(6,7) returns 7.
Math.max(-3,-2) returns -2
Math.max(-2,3) returns 3
Math.max(5.25,5.26) returns 5.26
The following code demonstrates the function of Math.max():
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
<html> <head> <script type="text/javaScript"> document.write(Math.max(6,7)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.max(-3,-2)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.max(-2,3)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.max(5.25,5.26)+"<br>"); </script> </head> <body> </body> </html> |
Min(x,y):
This method is used to find the minimum number of two numbers. The general syntax to use this method is:
Math.min(x,y);
Example:
Math.max(6,7) returns 6.
Math.max(-3,-2) returns -3
Math.max(-2,3) returns -2
Math.max(5.25,5.26) returns 5.25
The following code demonstrates the function of Math.min():
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
<html> <head> <script type="text/javaScript"> document.write(Math.min(6,7)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.min(-3,-2)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.min(-2,3)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.min(5.25,5.26)+"<br>"); </script> </head> <body> </body> </html> |
Cos():
This method returns the cosine of a given number. It returns a numeric value between -1 and 1, which represents the cosine of the angle. The general syntax to use this method is:
Math.cos(x);
Example:
Math.cos(3) returns -0.98999.
Math.cos(0) returns 1.
Math.cos(1) returns 0.5403023.
The following code demonstrates the function of Math.cos():
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
<html> <head> <script type="text/javaScript"> document.write(Math.cos(3)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.cos(0)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.cos(1)+"<br>"); </script> </head> <body> </body> </html> |
Sine():
This method returns the sine of a given number. The general syntax to use this method is:
Math.sin(x);
Example:
Math.sin(1) returns 0.8417.
Math.sin(0) returns 0
The following code demonstrates the function of Math.sin():
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
<html> <head> <script type="text/javaScript"> document.write(Math.sin(1)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.sin(0)+"<br>"); </script> </head> <body> </body> </html> |
Tan():
This method returns the tangent of given number. The general syntax to use this method is:
Math.tan(x);
Example:
Math.tan(1) returns 1.5574.
Math.tan(0) returns 0
The following code demonstrates the function of Math.tan():
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 |
<html> <head> <script type="text/javaScript"> document.write(Math.tan(1)+"<br>"); document.write(Math.tan(0)+"<br>"); </script> </head> <body> </body> </html> |