Java Type Conversion Or Java Type Casting
Table of Contents
Java Type Casting Or java Type Conversion:
Java Type Conversion– In this tutorial you will learn about type casting or type conversion. In computer science, type conversion, type casting, type coercion, and type juggling are different ways of changing expression from one data type to another. An example would be the conversion of an integer value into a floating-point value or its textual representation as a string, and vice versa. Type conversions can take advantage of certain features of type hierarchies or data representations. Two important aspects of a type conversion are whether it happens implicitly (automatically) or explicitly, and whether the underlying data representation is converted from one representation into another, or a given representation is merely reinterpreted as the representation of another data type. In general, both primitive and compound data types can be converted.
Amazon Purchase Links:
*Please Note: These are affiliate links. I may make a commission if you buy the components through these links. I would appreciate your support in this way!
Numeric Primitive Java Type Conversion or Type Casting:
Numeric primitives data can be cast in two ways. Implicit type casting happens when the source type has a smaller range than the target type.
Implicit casting
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
byte byteVar = 42; short shortVar = byteVar; int intVar = shortVar; long longVar = intvar; float floatVar = longVar; double doubleVar = floatVar; |
Explicit type casting has to be done when the source type has a larger range than the target type.
Explicit casting
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
double doubleVar = 42.0d; float floatVar = (float) doubleVar; long longVar = (long) floatVar; int intVar = (int) longVar; short shortVar = (short) intVar; byte byteVar = (byte) shortVar; |
When casting floating-point primitives data type (float, double) to whole number primitives, the number is rounded down.
Basic Numeric Promotion Java Type Conversion or Type Casting:
One special case of implicit type conversion is type promotion, where the compiler automatically expands the binary representation of objects of integer or floating-point types. Promotions are commonly used with types smaller than the native type
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
static void testNumericPromotion() { char char1 = 1, char2 = 2; short short1 = 1, short2 = 2; int int1 = 1, int2 = 2; float float1 = 1.0f, float2 = 2.0f; // char1 = char1 + char2; // Error: Cannot convert from int to char; // short1 = short1 + short2; // Error: Cannot convert from int to short; int1 = char1 + char2; // char is promoted to int. int1 = short1 + short2; // short is promoted to int. int1 = char1 + short2; // both char and short promoted to int. float1 = short1 + float2; // short is promoted to float. int1 = int1 + int2; // int is unchanged. } |
Non-numeric primitive Java Type Conversion or Type Casting
A boolean type cannot be cast to/from any other primitive type. the char can be cast to/from any numeric type by using the code-point mappings specified by Unicode. A char is represented in memory as an unsigned 16-bit integer value (2 bytes), so casting to byte (1 byte) will drop 8 of those bits (this is safe for ASCII characters). The utility methods of the Character class use int (4 bytes) to transfer to/from code-point values, but a short (2 bytes) would also suffice for storing a Unicode code-point.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
int badInt = (int) true; // Compiler error: incompatible types char char1 = (char) 65; // A byte byte1 = (byte) 'A'; // 65 short short1 = (short) 'A'; // 65 int int1 = (int) 'A'; // 65 char char2 = (char) 8253; // ‽ byte byte2 = (byte) '‽'; // 61 (truncated code-point into the ASCII range) short short2 = (short) '‽'; // 8253 int int2 = (int) '‽'; // 8253 |
Object Java Type Conversion or Type Casting
As with primitives, objects can be cast explicitly and implicitly. Implicit type casting happens when the source type extends or implements the target type (casting to a superclass or interface). Explicit type casting has to be done when the source type is extended or implemented by the target type (casting to a subtype). This can produce a runtime exception (ClassCastException) when the object being cast is not of the target type (or the target’s subtype).
|
1 2 3 4 |
Float floatVar = new Float(42.0f); Number n = floatVar; //Implicit (Float implements Number) Float floatVar2 = (Float) n; //Explicit Double doubleVar = (Double) n; //Throws exception (the object is not Double) |
Testing if an object can be cast using instanceof
Java delivers the instanceof operator to test if an object is of a certain type, or a subclass of that type. The program can then choose to cast or not cast that object consequently.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
Object obj = Calendar.getInstance(); long time = 0; if(obj instanceof Calendar) { time = ((Calendar)obj).getTime(); } if(obj instanceof Date) { time = ((Date)obj).getTime(); // This line will never be reached, obj is not a Date type. |
java type conversion or type casting Examples:
Example how to use java type conversion or type casting in Binary Numeric Promotion:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
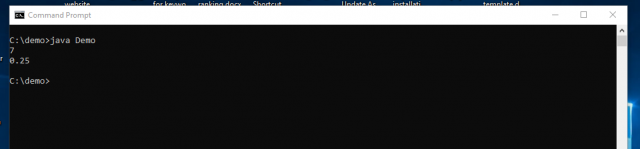
class Demo{ public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 0; float f = 1.0f; double d = 2.0; // First int*float is promoted to float*float, then // float==double is promoted to double==double: if (i * f == d) System.out.println("oops"); // A char&byte is promoted to int&int: byte b = 0x1f; char c = 'G'; int control = c & b; System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(control)); // Here int:float is promoted to float:float: f = (b==0) ? i : 4.0f; System.out.println(1.0/f); } } |
OutPut:
Example how to use java type conversion or type casting in Unary Numeric Promotion:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
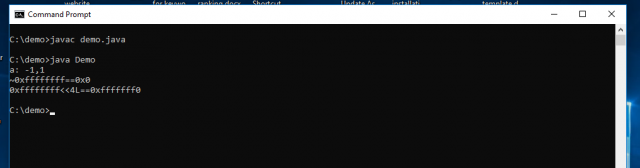
class Demo{ public static void main(String[] args) { byte b = 2; int a[] = new int[b]; // dimension expression promotion char c = '\u0001'; a[c] = 1; // index expression promotion a[0] = -c; // unary - promotion System.out.println("a: " + a[0] + "," + a[1]); b = -1; int i = ~b; // bitwise complement promotion System.out.println("~0x" + Integer.toHexString(b) + "==0x" + Integer.toHexString(i)); i = b << 4L; // shift promotion (left operand) System.out.println("0x" + Integer.toHexString(b) + "<<4L==0x" + Integer.toHexString(i)); } } |
OutPut:
Example how to use java type casting for Array Types in Java:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
class Point { int x, y; Point(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } public String toString() { return "("+x+","+y+")"; } } interface Colorable { void setColor(int color); } class ColoredPoint extends Point implements Colorable { int color; ColoredPoint(int x, int y, int color) { super(x, y); setColor(color); } public void setColor(int color) { this.color = color; } public String toString() { return super.toString() + "@" + color; } } class Demo{ public static void main(String[] args) { Point[] pa = new ColoredPoint[4]; pa[0] = new ColoredPoint(2, 2, 12); pa[1] = new ColoredPoint(4, 5, 24); ColoredPoint[] cpa = (ColoredPoint[])pa; System.out.print("cpa: {"); for (int i = 0; i < cpa.length; i++) System.out.print((i == 0 ? " " : ", ") + cpa[i]); System.out.println(" }"); } } |
OutPut: