Thermal Power Plant, Working of Thermal Power Plant, Largest thermal power Plants in the world
Table of Contents
Thermal power plant:
A Thermal power plant converts the chemical energy stored in the fossil fuels into electrical energy. Thermal power plant helps almost half of the world power demand. They use water as working fluid. Today’s power plants are capable to run under green efficiency by conforming to stringent environmental standards. Thermal power plant is place where the electricity generation takes place. In thermal power plant heat of coal combustion is converted into electricity. Coal is used as a fuel in thermal power plant. We know that when we are generating electricity we require alternator or generator.
Generator is a device which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. By turning the shaft of the generator we will be able to generate electricity. The generator derives motion from steam turbine the heart of the power plant. In order to turn the steam turbine, we have to apply high pressure and high temperature steam at the inlet of the turbine as the turbine absorbs energy from high energy fluid. Its pressure and temperature drop towards the outlet. High capacity power plants often use different stages of the steam turbines such as high pressure turbine, intermediate pressure turbine and low pressure turbine. So now we have met our objective, we have produced electricity from the generator.
When we bring the steam to original state which has low temperature and low pressure to high temperature and high pressure we can repeat the process.
The compressor will be used to raise the pressure but compressing steam is highly energy intensive process and such a power plant will not efficient at all.
The easy way to converts the steam into liquid and boost the pressure. For this purpose we will introduce condenser heat exchanger which set beneath the low pressure turbine. In the condenser a stream of cold water flows through the tubes. The steam rejects heat to the liquid stream and become condensed. Now we can use the pump to increase the pressure of this feed water. Typically multistage traffical pumping is used for this purpose that way the pressure will revert to its original state. The next task is to bring the temperature back to its original value. For this purpose heat is added to the exit of the pump with the help of a boiler.
Steam generation:
First we will boil the water which will require heat. This heat is provided by the burning the coal. When the water will boil it converted into steam.
There are different unit in the Thermal Power plant.
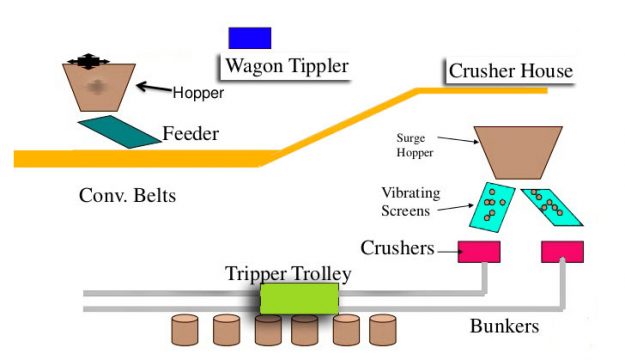
Coal storage:
We have coal storage in which coal is transferred from the coal mines. A 600MW power plant handles about 7200 tons of coal per day. Coal handling is to be flexible reliable and capable of handling large quantities in less time than even before. Coal plays a vital role in the generation of the electricity worldwide. Coal fired power plants currently fuel 41% of global electricity. Coal handling system is based on:
Coal delivery —–>Unloading—–> Weighting—–>Outdoor storage
Covered storage—–>In plant handling—–>Preparation—–>Transfer
Furnace transferring
Outdoor plant handling:
Outdoor plant handling means transfer of coal from mine or port to storage of coal at plant site.
- Transportation of coal by train: 4000 to 13000 tons/trip.
- Transportation of coal by ships: 45 million tons/year.
- Transportation of coal by roads: trucks etc.
- Transportation of coal by conveyor belts.
Coal weighting:
The load cell technology is used in the weighing which is the only genuine recognized method of long term accurate and reliable train weighting and uses the exact principal as the weight bridge, truck scales and every other general scale is based upon.
There are two types of storage:
-
Live Storage(boiler room storage):
In live storage the coal is stored for one or two days requirement of the power plant. Storage from which coal may be withdrawn to supply combustion equipment with little or no remanding is live storage and should have low maintenance. This storage consists of about 24 to 30 hours of coal requirements of the plant and is usually a covered storage in the plant near the boiler furnace which required a large amount of coal to burn. The live storage can be provided with bunkers and coal bins and it should be simple so that it can easily be transfer from one place to another. This storage is used for the purpose of supplying the coal to the combustion equipment with negligible handling. Bunkers are enough capacity to store the requisite of coal which is usually in vertical cylinder shape. The coal is transfer from bunkers transferred to the boiler grates.
-
Dead storage– stored for future use:
The coal is usually kept on ground in the form of pile which are sealed with fine coal and exposed to outside weather. It should be protected from weathering. Mainly it is for longer period of time, in dead storage we have store the coal about 30 to 80 days so that plant is never required to be shut down and it is also mandatory to keep a backup of fuel for specified amount of days depending on the reputation of the company and its connectivity there is risk of spontaneous combustion. The coal is required to be protected from deterioration and weathering. There is also possibility of loss deterioration during storage. Storage of coal allows the purchaser to take the advantage of the seasonal market fluctuation in prices of coal. This is long term storage i.e 10% of annual consumption. There are many forms of storage some of which are:
- Stacking the coal is the process in which the coal is kept in heaps over available open ground areas.
- But placed under cover or alternatively in bunkers.
- Allocating special areas and surrounding these with high reinforced concerted retaking walls.
Coal handling Plant:
From the coal storage plant the coal is transfer to the coal handling plant. In the coal handling plant the coal is heated and converted into pulverized coal so it crushed into small powder so the rate of combustion can increase then this powder coal is sent to the boiler.
In-plant coal handling:
The inplant coal handling system deals with the feeding of coal from the live storage to the furnace. It includes various equipment for transfer of coal like conveyor belt and equipment to weigh the quantity of coal to feed. In case of pulverized coal firing system. It requires large no of equipment like chutes, pulverized mills, feeders, weighing machine, hoppers and automatic scales.
Coal preparation:
The coal that came from the mines is of different shapes and sizes which is called uncrushed coal. So first the uncrush coal is put in the coal crusher. The coal is reduce to optimal size by the crushers. It is crushed into pieces of 25-30mm for stroke firing and 10-20mm for pulverized coal firing. Then it moves towards the vibrating separator where the coal particles vibrate. The size of vibrating separator if fitted after crusher to screen the coal crushed below set size. Vibrator separator separate the oversized coal which is of different size and is returned to crusher for further proper crushing. Then it moves towards the conveyor belt which transfers the coal to the coal drier. The moisture in the coal is removed through hot gases. Then this coal transfer through conveyor belt to the bucket elevator.
Transfer of coal:
- Conveyor belt
- Screw conveyor
- Bucket elevator
- Grab bucket elevator
- Flight conveyor or scrapers
- Skip hoist
Conveyor belt:
It consists of endless belt of suitable material running over pair of end drums supported at regular interval by series of rollers. It maximum inclination is 20 degree. Its running speed is about 400-500 RPM. Transport capacity is 50-100 ton/hour over long distance. It has low cost and power consumption. It has Smooth and clean operation. It has controlled rate of coal transfer.
Screw conveyors:
It is used for shorter distance 30m. It is totally enclosed from atmosphere. Coal dust can also be transferred easily. It has diameter of 15-20 cm and speed 70-120 rpm. Its transfer capacity is 100 tons/hour. It has high power consumption per coal of transfer.
Bucket elevator:
In bucket elevator coal is lifted vertical or near vertical direction. It carries bucket fixed to a chain. Buckets are loaded with coal at bottom and discharge at the top.
The lift of the coal is limited to about 30 m. inclination is limited to 60 degrees with horizontal. Transfer capacity 60 tons/hour.
Grab bucket elevator:
It transfer coal on a single rail or track from one point to the other. It can be used with crain or tower. Its transfer capacity is about 50 tons per hour. It requires less power for operation and minimum maintenance. It is used when other arrangements are not possible.
Flight conveyors or Scrapers:
It is generally used for transfer of coal when filling of number of storage bin under the conveyor is required. The coal is discharge at the bottom of trough. Transfer capacity is about 10 to 100 tons per hour.
In thermal power plant the coal is first grind into powder which burns faster and produces more heat. After grinding hot air is passed through it to remove moisture from it. The pulverized coal is transfer to the boiler.
Boiler:
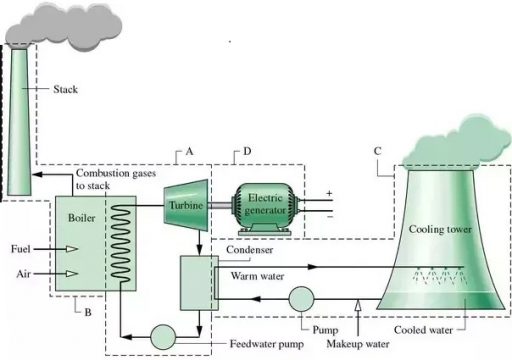
In boiler the chemical energy of the coal is converted into heat energy. In most thermal power plants water tube boiler are used. This type of boiler is used when we require a lot of steam at very high pressure. Because a steam turbine requires steam at very high pressure. The boiler can be greater 50 meters in height. The water is fed to the boiler in order to generate steam. We have make up water inlet. Make up water feeds to a deaerator. When we discuss the make-up water, we are discussing about the water that is added to the system and then treated before it becomes boiler feed water. We cannot just take water from a city grid or from a lake or a river and put it into a water tube boiler, which will not work. We will face many problems and corrosion. So this make up water has to be treated, chemically and mechanically and we do that quite often in a deaerator. The deaerator is going to decrease the oxygen and carbon dioxide content of the water and before the water gets to the deaerator, it is going to be filtered to take those particles that might be floating around in the water.
The boiler feed water pump is usually a multistage centrifugal pump and we will increase the pressure of our boiler feed water and send it to water tube boiler. The pressure involved here are actually quite high. The pressure is in excess of 200 bar. The water will be pumped to an economizer. Where we will preheat the water a little bit before we send it to the main body of the water tube boiler. We do not feed cold water to the main part of the boiler. If we do that then we will thermal shock the boiler and that could mean that we have cracked the pipes. We will then send the water around to the furnace and we will put the water into the water tube boiler walls. They are called walls because the piping around the furnace makes up a square space similar to having four separating walls. This means that we get a lot of heat transfer, mostly via radiation to the furnace walls and then this heat is going to be absorbed via conduction into the water and water is going to change in steam.
The boiler has miles of tubes which has high quality of water. The boiler is very important unit of the thermal power plant. Once inside the boiler the coal ignites releasing energy and generating intensity. In boiler the coal combustion takes place. The water in the pipes of the boiler is change into steam. The temperature of the steam is about 1000 degrees Fahrenheit. This process generate thermal energy which is converted into mechanical energy.
High capacity power plants generally use a type of boiler called a water tube boiler. Pulverised coal is burnt inside the boiler. The incoming water initially passes through any economizer session. Here the water will capture the energy from the flue gas the water flow from the down comer and then through water walls where transform into steam.
We have different types of steam:
- Wet steam
- Dry steam
- Super-heated steam
When we discuss about wet and dry steam we are referring to if steam has water molecules in it or not. If the steam is totally dry then it will have no water molecules in it. Steam is colourless and odourless gas and by the time this steam vapour has reached the steam drum which is at the top of the boiler then we have a wet steam. This steam is not completely drier it has particles of moisture in the steam. The pure stream is separated at a stream drum. Now the working fluid is back to its original state high pressure and high temperature this steam can be fed back into the steam turbine. The power production is continuous by repeating this cycle over and over again. This burning of coal produces ash and exhaust gases. The ash fall at the bottom of the boiler and is removed by the ash outlet system. This ash is usually use in building as ingredient like concrete etc.
The heat is generated and that heat is used to raise the temperature of water and then this water is converted into steam. Then the steam generated in the boil move towards steam turbine.
Steam turbine:
In steam turbine the steam is again super-heated after generating in the boiler and then it is converted in higher super steam. In case of super heating even after the liquid has been converted into steam even more heat is added and with that the steam become super-heated about 550C temperature. The higher the temperature of the steam the more efficient will the cycle. This high super steam is evaporated to the turbine and turbine starts rotation.
The steam turbine rotates 3600 times per minute. The steam turbine is mechanical coupled with the generator. When the turbine rotates the generator or alternator also rotates.
Thus the alternator converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy. Then this electrical energy is step-up through step-up transformer and transfer to the grid station. After the work done of the steam generator the pressure of the steam is reduced and is sent to the condenser.
Condenser:
After the steam has been used to create the electricity. It is exhausted from the turbine to the condenser. In the condenser the water is sprinkled on that steam and the steam is again converted into water. Then the same water is given to the boiler. This water is again reused.
After the combustion various gases are generated. But a power plant working on this basic Rankin cycle will have a very low efficiency and a low capacity. We can increase the performance of the power plant considerably with the help of few simple techniques.
- Super heating
- Reheating
- Feed water heating
Just remember the Carnot theorem of maximum thermal efficiency of any engine can be limited this is possible but the steam turbine material will not withstand the temperature of more than 600 degrees Celsius. So super-heated is limited to the threshold maximum bearable temperature 600C. The temperature of the steam decreases as it flows along the rows of the blade. Consequently a great way to increase the efficiency of the power plant is to add more heat after the first turbine stage
Exhaust gas system:
The exhaust gas system is also known as flue gas system. The exhaust gas will pass through the preheater and some of the remaining of the heat from the exhaust gases. It is use to heat up the air which is being fed to the boiler. After that the exhaust gas will pass to electrostatic precipitator and will effectively ionize the exhaust gas stream in order that particles are attracted to large metal plates. These metal plates have a large contact surface area. Particles in the exhaust gas stream such as fly ash will be attracted to these large surfaces and in this way we can remove them from the exhaust gas steam. Periodically these large plates will become totally covered in these exhausts gas particles and will shape the plates or simply bang them in order that the particles fall of the plates and then go to the silo where they can be discharged to a truck or maybe they will go to an ash pond or some sort of landfill sites. The particles that filter out via the electrostatic precipitator can actually be sold and they will often use these particles in the cement industry for example. So they will ship the particles off to a cement plant.
After the electro precipitator the exhaust gases pass through an induced draft fan and then they will flow to a desulphurization gas scrubber. The idea with the scrubber is that we are removing as much of the sulphur dioxide from the gas stream as possible before we discharge the exhaust gas to the atmosphere. In order to remove the sulphur from the gas stream, we will usually use lime, limestone or ammonia and we will spray that into a large column, it will absorb some of the sulphur we may get ammonia sulphate for example and will form something called gypsum which can then also be sold. After flue gas desulphurization the exhaust gases then flow to a stack which is large cylindrical steel column much like a chimney and the exhaust gases will be discharged to atmosphere. We call it stack because of the stack effect which essentially means that hot air will rise above the cooler air due to the density difference.
Advantages of thermal power plant:
- It has less initial cost as compared to other power plants
- The main fuel in thermal power plant is coal which is quite cheap
- It required less space as compared to hydroelectric power plants
- It can be installed at any place irrespective of the existence of the fuel while the hydroelectric power plants can be develop only at the source of the water supply
- Thermal power plants are able to respond to rapidly changing loads without difficulty
- The cost of generation is less than that of the diesel power station
- Thermal power plants can withstand for overload with certain extent
- They form the backbone of grid as they provide stable output and are able more reliable than renewable sources that tends to fluctuate
- A portion of steam raise can be used as process steam in various industries such as sugar mills, paper mills, refineries, textile mills, plastic manufacture and chemical work etc.
- The technology for the thermal power plant is easily accessible and well established not like other sources like nuclear, solar, hydroelectric, wind power plant etc.
Disadvantages of thermal power plants:
- Thermal power plant are not environment friendly and plants emit toxic pollutants like ash, carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide
- This type of power station ultimately responsible for raise in the water sea level
- The machines and boilers in thermal power plants are intricate and complicated. So occurrence of the mechanical trouble is more frequent maintenance and operating cost is high.
- It pollutes the atmosphere due to the production of large amount of smoke and fume.
- Disposal of ash is quite difficult
- Requires huge quantity of water
- Handling of coal is difficult
- It is very difficult to maintain optimum supply for a long period
- Thermal engine requires huge amount of lubricating oil that is very expensive
- The heated water disturbs the ecology and has adverse effect on the lives that comes from thermal power plants
- Transportation of the fuels is one of the major difficulty for the plants located away from coal fields
- Starting is quite longer than other power plants.
Largest power plants in the world
-
Datang Tuoketuo Power Station:
It is located in China. It has capacity of 6720MW. It used bituminous type of coal. It provides power to the Beijing.
-
Taean Power station:
It is located in South Korea. It has capacity of 6100MW. It used bituminous type of coal.
-
Dangjin power station:
It is located in South Korea. It has capacity of 6040MW. It used bituminous type of coal.
-
Taichung power station:
It is located in Taiwan. It has capacity of 5500MW. It used bituminous and subbituminous type of coal.
- Belchatow power station:
It is located in Poland. It has capacity of 5420MW. It used lignite type of coal.
-
Waigaoqiao power station:
It is located in China. It has capacity of 5160MW. It used bituminous type of coal.
-
Yeoncgcheung Power station:
It is located in China. It has capacity of 5080MW. It used bituminous type of coal.
-
Guodian Beilun Power station:
It is located in China. It has capacity of 5060MW. It used bituminous type of coal.
-
Guohua Taishan power station:
It is located in China. It has capacity of 5000MW. It used bituminous type of coal.
-
Jiaxing Power station:
It is located in China. It has capacity of 5000MW. It used bituminous type of coal.