Lead acid battery, Construction and, Working, and Charging
Table of Contents
Lead Acid Battery Introduction:
Lead Acid Battery– The type of battery which uses lead peroxide and sponge lead for the conversion of the chemical energy into electrical energy, such type of the electric battery is called a lead acid battery. Because it has higher cell voltage and lower cost, the lead acid battery is most often used in power stations and substations. Read my article on how to make your own high ampere large Lead Acid battery, this article also explains what tools you should have and how to use them.
What is Battery?
The type of devices in which the Chemical Energy is converted into Electrical Energy are called electric cells. When a specific number of these electric cells are electrically connected in Series and Parallel combinations it forms a Battery. Basically each electric cell is made of two different or dissimilar conductors that are immersed in the conducting solution. So, an electric Battery is such a type of electrochemical device that converts the chemical reactions happening among the electric cells into electrical energy. A battery can have one or more electrochemical cells with external connections called electrodes for powering electrical devices such as UPS, Mobile Phones, Flashlights, and Electric Cars, etc. The electrodes are normally marked with + and – signs.
Without any further delay let’s get started!!!
Batteries Available on Amazon:
Hydrometer for the Lead Acid Battery
Other Tools and Components:
Super Starter kit for Beginners
PCB small portable drill machines
*Please Note: These are affiliate links. I may make a commission if you buy the components through these links. I would appreciate your support in this way!
Types of Battery:
Normally, there are two types of batteries
- Primary Battery
- Secondary Battery
I have already explained in very detail about the primary batteries and secondary batteries. You should definitely read this article.
Lead acid Cell:
The lead acid cell was invented in 1859 by French physicist Gaston Planté and is the earliest type of rechargeable battery. Despite having a very low energy-to-weight ratio and a low energy-to-volume ratio, its ability to supply high surge currents means that the cells have a relatively large power-to-weight ratio. These features, along with their low cost, make them attractive for use in motor vehicles to provide the high current required by starter motors.
The Lead acid storage cell +ve plate is made of lead peroxide (PbO2) and the negative plate is made of Sponge Lead i.e Pb. Light Sulfuric acid is used as the electrolyte. When the Lead acid cell supply current to a load or the Lead acid cell discharges a chemical reaction occurs, as a result of which lead sulfate is created on both the plates, and the electrolyte is converted into water. After the discharge process both the plates are converted into the same type of material, due to which the battery cannot produce enough voltage to power up the electrical loads.
Now to charge the Lead acid cell current in the opposite direction is applied, this way the chemical reaction is reversed and once again the +ve plate becomes Lead peroxide and the negative plate become pure lead, during the same process the electrolyte is also restored i.e electrolyte becomes sulfuric acid.
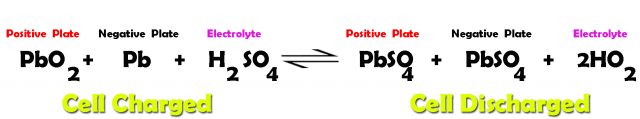
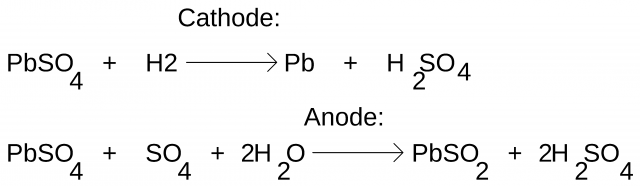
The charging and discharging chemical reaction of the lead acid cell can be written as.
Reading the above equation from left to right represents the cell discharging action, and when the same equation is read from right to left it represents the cell charging action. During the cell discharging lead peroxide, lead, and sulfuric acid undergoes a chemical reaction and are converted into lead sulfate and water. During the cell charging the lead sulfate is converted back into lead peroxide, lead, and sulfuric acid. The average terminal voltage of the lead-acid battery is approximately 2.2V.
Lead acid Cell Working Principle:
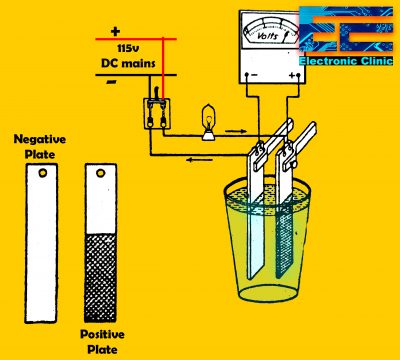
The working principle of the lead acid cell can be explained with the help of a simple experiment.
As you can see in the diagram above, two lead strips are immersed in the dilute sulfuric acid having specific gravity approximately equal to 1.200. One lead strip is the positive plate and the other lead strip is the negative plate. These positive and negative plates are connected in series with a lamp. The plates and lamp are connected with the external 115v DC. When the DC power supply is turned ON an electric current will start flowing due to which the strips or electrodes start producing bulbs. After some time the color of one of the plates will become dark chocolate type, while the color of the other plate will remain the same, but if you will pay concentration you will find that the other plate solid lead surface is now converted into a Spongy lead.
When the cell is supplied power, the cell starts charging and the voltmeter shows approximately 2.5 volts. But as the cell starts discharging, then the cell voltage is dropped to approximately 1.75, this voltage drop speeds up and soon the voltmeter shows zero on the dial, and the dark brown chocolate color plate is converted into a light color plate and soon retains its original color.
The Dark chocolate plate is the positive plate or cathode. The plate which is fractionally converted into a Spongy lead is the negative plate or Anode. The majority of the bubbles are produced by the negative plate, which represents the Oxygen gas. In this type of cell when the current flows, it changes the metallic lead into lead peroxide while there is no chemical change in the negative plate. The negative plate changes from solid shape to Spongy lead shape. When the cell produces electric current then the peroxide of the positive plate is converted into lead sulfate and the Spongy lead is also converted into lead sulfate, so electrochemically both the plates become the same.
So, as both the plates are electrochemically the same no voltage is produced and the cells are discharged. Again through the process of charging, the electric current converts the positive plate into the peroxide and the negative plate is converted into the Spongy lead, this way both the plates become dissimilar, due to which the voltage is produced, this voltage is around 2.05. During the charging process, the battery terminals should have 2.50V to control internal resistance and polarization. Remember, when the battery is charging, the only change in the electrolyte is that, the battery water starts converting into sulfuric acid, in this way due to the battery charging the specific gravity is increased. During the cell discharging lead peroxide, lead, and sulfuric acid undergoes a chemical reaction and are converted into lead sulfate and water and the specific gravity of the electrolyte is reduced. During the charging process, the negative plate produces hydrogen and the positive plate produces Oxygen. As hydrogen is flammable so during the process of charging keep it away from the fire.
Construction of Lead-acid battery or lead-acid storage battery:
We know, a lead acid storage battery is made by connecting multiple lead acid cells in series or parallel. The capacity of the lead acid storage battery depends on the number of the lead acid cells used. Any custom size lead acid battery can be made if you know about the connections.
There are basically two parts of the lead-acid battery.
- container and
- plates
Lead-acid battery Container:
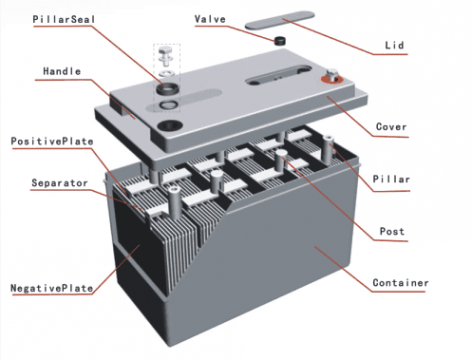
Since this battery container primarily contains sulfuric acid as an electrolyte, the materials used to make a lead-acid battery container must be sulfuric acid-resistant. The container material should also be free from those impurities which deterious to the sulfuric acid. Especially Iron and manganese are intolerable. That’s why the container of the lead acid battery is usually made of lead lined wood, glass, ebonite, the hard rubber of bituminous compound, ceramic materials and molded plastic parts, Using the above properties, therefore, the lead-acid battery container is made of either of these materials. The container is tightly sealed with top cover. The top cover has three holes, one at each end for the posts and one in the middle for vent plug and through which the electrolyte is poured and gases escape out.
There are two ribs to hold the positive lead acid battery plates inside the bottom floor of the lead acid battery container and two other ribs to hold the negative plates. The ribs or prisms serve as supports for the plates, thus shielding them from short circuits that would otherwise occur as a result of the collapse of the active material from the plates to the container’s bottom.
Lead-Acid battery Plates:
The lead-acid cell plate has diverse design, and they all consist of some sort of a grid consisting of lead and the active material. The grid is essential if the electrical current is to be conducted and the current is to be distributed equally on the active material. If the current is not distributed evenly then the active material loosens and falls out.
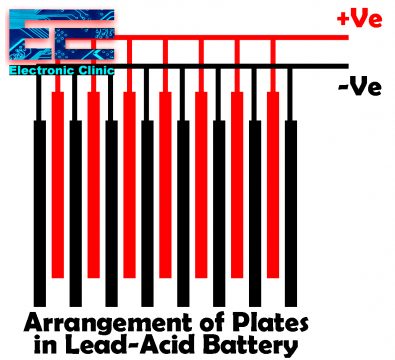
All the plates are connected in the positive and negative groups so that the final connections can be easily done. The negative plates are greater in number than the positive plates. As you can see in the diagram above, each positive plate is sandwiched between two negative plates, this is done so that the chemical reaction could take place on both sides of the positive plates. This also protects the plates from Buckling. Separators are placed between the positive and negative plates, these separators are made up of wood, rubber, or glass mat, that protects the positive and negative plates from making physical contact.
One side of the separator is smooth while the other side of the separator is grooved. The grooved side is placed against the positive side of the plate so that the electrolyte solution can easily move around as most of the chemical reaction occurs on this side.
The lead-acid battery plates are of the two types
- Formed plates or Plante plates
- Pasted or faure plates.
Plante’s plates are mainly used for stationary batteries, as they are higher in weight and more costly than the pasted plates. But the plates are more durable and less likely to lose active material by quick charging and discharging. The plantes plate has a low capacity weight-ratio.
The Faure process is much more suitable for producing negative plates than positive plates. The negative active substance/material is rather strong, and it undergoes a comparatively low change from charging and discharging.
- Positive Plate
- Negative Plate
- Separators
- Electrolyte
- Element
- Cell covers and Vent plugs
- Battery Terminals
- Cell Connectors
- Container
Positive and Negative plates:
The grids contain an alloy of lead and antimony. These are usually made with the transverse rib that crosses the places at a right angle or diagonally. The grid for the positive and negative plates is of the same design, but the grids for the negative plates are made lighter because they are not as critical to the current’s uniform conduction.
Separators:
Separators are placed between the positive and negative plates, these separators are made up of wood, rubber, or glass mat, that protects the positive and negative plates from making physical contact. One side of the separator is smooth while the other side of the separator is grooved. The grooved side is placed against the positive side of the plate, so that the electrolyte solution can easily move around as most of the chemical reaction occurs on this side.
Electrolyte:
Dilute Sulfuric Acid H2SO4 is used as an electrolyte. It contains only 31% of the sulfuric acid. I have already explained this in very detail through a chemical equation.
Element:
In any cell, the assembly of positive and negative plates is called an element.
Container, Cell covers, and vent plugs:
I have already explained the battery container above.
Battery terminals:
Every Lead acid battery is provided with two terminals which are called the battery terminals. These battery terminals are marked with + and – signs. The +Ve terminal is usually larger than the negative terminal.
Cell connectors:
Cell connectors are used to connect the individual cells in series to achieve the desired voltage.
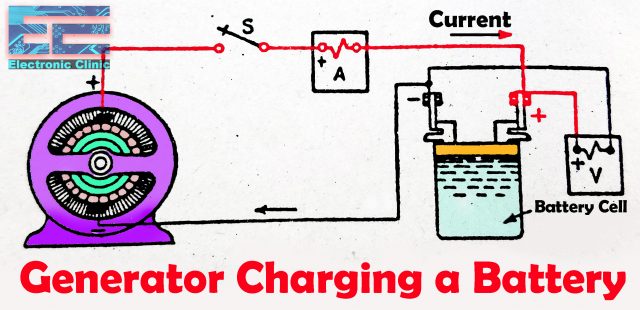
Charging of lead acid battery:
A new or discharged lead acid battery is charged using a DC charger, the voltage supplied is greater than the battery voltage. The charging process continues until the battery is fully charged. The current will flow through the battery in the reverse direction to when it is supplying current and the battery will charge. The positive and negative terminals of the battery are connected with the dc power supply positive and negative terminals. Double-check the positive and negative wires of the dc power supply before you are going to charge the battery.
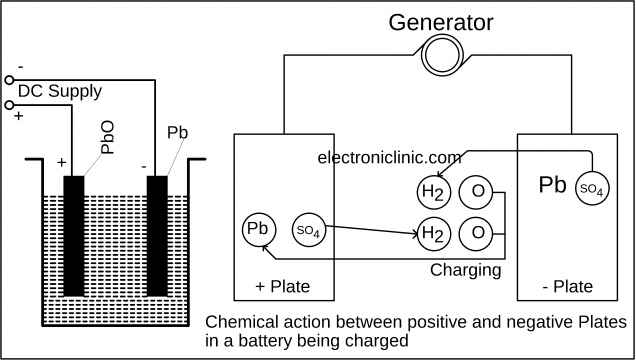
While charging a battery for the first time use a low-density electrolyte and slowly charge the battery. The H2 ions are attracted towards the cathode and SO4 ions move towards the anode. As you can see in the picture below.
The following changes occur during the charging:
- The anode color is changed to Dark chocolate color and the cathode color is changed to Grey.
- The specific gravity of the sulfuric acid is increased from 1.18 to 1.27.
- The cell voltage is increased from 1.8V to 2.3V.
- The cell starts absorbing the energy.
- When the charging is completed then the cell starts producing the gas.
To charge a battery the Generator or Battery charger electric pressure should be at least 25% greater than the battery voltage. Let’s say for a 12v battery the charger voltage should be 15 volts. Battery should not be charged with more current, because it can damage the battery. However, once a battery has been charged to its full capacity, it is important not to continue charging as this will damage the battery. A charge controller is necessary to ensure that the battery is not overcharged. Most of the batteries are damaged due to the overcharging, this usually happens when the batteries are charged using the solar panels. What people usually do, they simply connect the solar panels with the battery and don’t use the solar charge controller.
A charge controller or charge regulator is basically a voltage or current regulator to keep batteries from overcharging. It regulates the voltage and current from the solar panels going to the battery. Most 12 volt panels put out about 16 to 20 volts or even more, so if there is no regulation the batteries will be damaged from overcharging as most batteries need around 14 to 14.5 volts to get fully charged. If you are planning to use a solar panel then purchasing the solar charge controller should be the first priority. I have a very detailed article on this; you should definitely read this article.
What is a Solar charge controller and it’s wiring.
Before charging the battery, it is necessary to check the specific gravity of the electrolyte, if the specific gravity of the acid is less than 1.175 then the electrolyte should be changed. The vent plugs should be removed while charging the battery so that the hydrogen gas can escape which is produced during the charging process.
Methods of battery charging:
- Constant Current Method
- Constant Potential Method
Lead Acid Battery Efficiency:
The Lead Acid battery is not 100 percent effective in electricity storage – you are never going to get out as much as you put in when charging. Overall, the performance standard is often believed to be 85 percent. The performance would depend on a number of variables including the charge rate or discharge rate. The higher the rate of charge or discharge, the lower the efficiency. The state of charge of the battery will also affect charge efficiency. With the battery at a half charge or less, the charge efficiency may be over 90%, dropping to nearer 60% when the battery is above 80% charged. However, it has been found that if a battery is only partially charged, efficiency may be reduced with each charge. If this situation persists (the batteries never reaching full charge), the life of the battery may be reduced.