GSM Sim900A with Arduino Complete Guide with GSM based Projects Examples
Table of Contents
GSM Sim900A Description:
GSM Sim900A– the GSM SIM900A by the SIMCom is designed for global market, SIM900A is a dual-band GSM/GPRS engine that works on frequencies EGSM 900MHz and DCS 1800MHz. SIM900A features GPRS multi-slot class 10/ class 8 (optional) and supports the GPRS coding schemes CS-1, CS-2, CS-3 and CS-4.
With a tiny configuration of 24mm x 24mm x 3mm, SIM900A can meet almost all the space requirements in your applications, such as M2M, smartphone, PDA, and other mobile devices.
The physical interface to the mobile application is a 68-pin SMT pad, which provides all hardware interfaces between the module and customers’ boards.
The SIM900A is designed with power saving technique so that the current consumption is as low as 1.5mA in SLEEP mode.
The SIM900A is integrated with the TCP/IP protocol; extended TCP/IP AT commands are developed for customers to use the TCP/IP protocol easily, which is very useful for those data transfer applications.
Amazon Links:
Arduino Nano USB-C Type (Recommended)
Other Tools and Components:
ESP32 WiFi + Bluetooth Module (Recommended)
Super Starter kit for Beginners
PCB small portable drill machines
*Please Note: These are affiliate links. I may make a commission if you buy the components through these links. I would appreciate your support in this way!
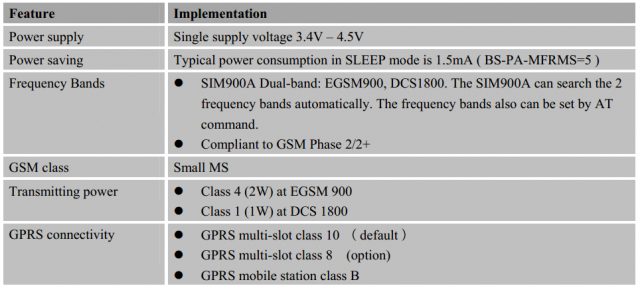
SIM900A key features:
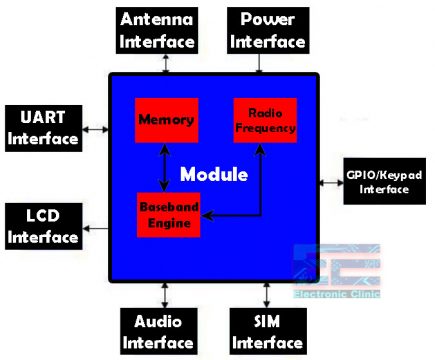
GSM SIM900A Functional Diagram:
The above figure shows a functional diagram of the SIM900A and illustrates the mainly functional parts:
- The GSM baseband engine
- Flash and SRAM
- The GSM radio frequency part
- The antenna interface
- The Other interfaces
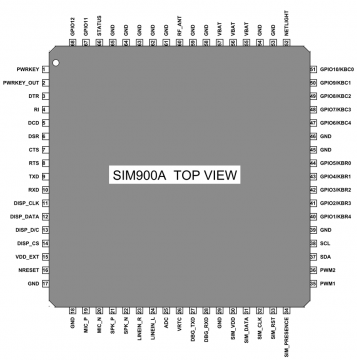
GSM SIM900A Pin Description:
GSM SIM900A by the SIMCom is a 68 terminal device as shown in the pin diagram given above. I will describe the function of each pin.
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
| 1 | PWRKEY | Voltage input for PWRKEY. PWRKEY should be pulled low to power on or power off the system.
The user should keep pressing the key for a short time when power on or power off the system because the system need margin time in order to assert the software. |
| 2 | PWRKEY_OUT | Connecting PWRKEY and PWRKEY_OUT for a short time then release also can power on or power off the module. |
| 3 | DTR | Data terminal Ready [Serial port ] |
| 4 | RI | Ring indicator [Serial port ] |
| 5 | DCD | Data carry detect [Serial port ] |
| 6 | DSR | Data Set Ready [Serial port ] |
| 7 | CTS | Clear to send [Serial port ] |
| 8 | RTS | Request to send [Serial port ] |
| 9 | TXD | Transmit data [Serial port ] |
| 10 | RXD | Receive data [Serial port ] |
| 11 | DISP _CLK | Clock for display [Display interface] |
| 12 | DISP_DATA | Display data output [Display interface] |
| 13 | DISP _D/C | Display data or command select [Display interface] |
| 14 | DISP _CS | Display Enable [Display interface] |
| 15 | VDD_EXT | 2.8V output power supply |
| 16 | NRESET | External reset input |
| 17,18,29,39,45,
46,53,54,58,59, 61,62,63,64,65 |
GND | Ground |
| 19 | MIC_P | Microphone Positive |
| 20 | MIC_N | Microphone Negative |
| 21 | SPK_P | Speaker Positive |
| 22 | SPK_N | Speaker Negative |
| 23 | LINEIN_R | Right Channel input [External line inputs are available to directly mix or multiplex externally generated analog signals such as polyphonic tones from an external melody IC or music generated by an FM tuner IC or module.] |
| 24 | LINEIN_L
|
Left Channel Input |
| 25 | ADC | General purpose analog to digital converter. |
| 26 | VRTC | Current input for RTC when the battery is not supplied for the system.
Current output for backup battery when the main battery is present and the backup battery is in low voltage state. |
| 27 | DBG_TXD | Transmit pin [Serial interface for debugging and firmware upgrade ] |
| 28 | DBG_RXD | Receive pin [Serial interface for debugging and firmware upgrade ] |
| 30 | SIM_VDD | Voltage supply for SIM card |
| 31 | SIM_DATA | SIM data output |
| 32 | SIM_CLK | SIM clock |
| 33 | SIM_RST | SIM reset |
| 34 | SIM_PRESENCE | SIM detect |
| 35 | PWM1 | PWM Output |
| 36 | PWM2 | PWM Output |
| 37 | SDA | Serial Data [I2C] |
| 38 | SCL | Serial Clock [I2C] |
| 40,41,42,43,44
& 47,48,49,50,51 |
KBR0 to KBR4
& KBC4 to KBC0 |
Keypad interface [ROWS & COLUMNS] |
| 52 | NETLIGHT | Indicate net status |
| 55,56,57 | VBAT | Three VBAT pins are dedicated to connect the supply voltage. The power supply of SIM900A has to be a single voltage source of VBAT= 3.4V to 4.5V. It must be able to provide sufficient current in a transmit burst which typically rises to 2A. |
| 60 | RF_ANT | Antenna connection |
| 66 | STATUS | Indicate working status |
| 67 | GPIO 11 | General Purpose Input/output |
| 68 | GPIO 12 | General Purpose Input/output |
GSM SIM900A Applications
- Cellular Communication
- Home Automations
- Security based projects
- Sensors monitoring
- Robotics
- Mobile Phone Accessories
- Servers
- Computer Peripherals
- Automobile
- USB Dongles
How to use the SIM900A:
It’s seems quite impossible for a beginner to do all the soldering, I will never do this, in fact I don’t have to do this, because readymade modules are already available in the market.
GSM Sim900A Module:
This is the GSM Sim900A mini Module. The first thing that you will notice about this GSM module is that, it has no onboard voltage regulator, so be very careful while applying the voltage; Because voltages greater than 5 volts can easily damage this module. Ideal voltage for this GSM module is 4.7v but you can easily power up this GSM Sim900A module using a 5v adaptor. if you don’t have a 5v adaptor then you can make your power supply using lm317t adjustable variable voltage regulator, I have a very detailed tutorial on lm317t explaining everything.
There are a few things that I really like about the GSM sim900A module which are
- This is the cheapest GSM module available on the Market.
- Another cool thing is, it can be easily interfaced with 5V supported controller boards like Arduino Uno, Arduino mega, Arduino Nano etc and also with 3.3v controller boards like Nodemcu ESP8266 Wifi Module and ESP32 etc. The GSM Sim900A module interfacing with Nodemcu ESP8266 and ESP32 will be explained in one of my future articles.
GSM Sim900A specifications:
GSM Sim900A Power Supply:
As I said earlier the GSM Sim900A Module has no onboard voltage regulator. Although it has a power supply pin which can be connected with the Arduino’s 5 volts. When no sensors are connected with the Arduino then you can Run this GSM module without any problem. But the time you start connecting different sensors with the Arduino, then Arduino cannot provide enough current to the Sim900A Module due to which the Arduino starts resetting.
So, my recommendation is use an external regulated 5v power supply.
GSM Sim900A pin configuration:
The white connector labeled with 4.7 – 5V, This is where we connect the external 5volt regulated power supply. It has a total of 9 male headers. The three male headers on the right side are not connected.
- Pin number 1 is the VCC which can be connected with the Arduino’s 5volts. In my case as I will power up this module using the external power supply so I will leave this pin unconnected.
- Pin number 2 is the ground, which will be connected with the Arduino’s ground.
- Pin number 3 is the 5v TXD,
- Pin number 4 is the 5v RXD,
- Pin number 5 is the 3.3v TXD, and
- Pin number 6 is the 3.3v RXD.
GSM Sim900A AT commands:
TO CHECK THE MODEM:
AT
OK
TO CHANGE SMS SENDING MODE:
AT+CMGF=1
OK
TO SEND NEW SMS:
AT+CMGS=”MOBILE NO.”
<MESSAGE
{CTRL+Z}
PREFERRED SMS MESSAGE STORAGE:
AT+CPMS=?
+CPMS: (“SM”),(“SM”),(“SM”)
OK
AT+CPMS?
+CPMS: “SM”,19,30,”SM”,19,30,”SM”,19,30
TO MAKE A VOICE CALL:
ATD923339348223;
TO REDIAL LAST NO:
ATDL
TO RECEIVE INCOMING CALL:
ATA
TO HANGUP OR DISCONNECT A CALL:
ATH
OPERATOR SELECTION:
AT+COPS=?
OK
AT+COPS?
+COPS: 0,0,”AirTel”
OK
TO SET A PARTICULAR BAUDRATE:
AT+IPR=? {To view the baud rate values}
AT+IPR=0 {To set the modem to autobauding mode}
READ OPERATOR NAMES.
AT+COPN=?
OK
AT+COPN
+COPN: “472001”,”DHIMOBILE”
+COPN: “60500
+COPN: “502012”,”maxis mobile”
+COPN:
+COPN: “502013”,”TMTOUCH”
+COPN
+COPN: “502016”,”DiGi”
+COPN: “502017”,”TIMECel””
+COPN: “502019”,”CELCOM GSM”
AT+CRC SET CELLULAR RESULT CODES FOR INCOMING CALL INDICATION:
AT+CRC=?
+CRC: (0-1)
OK
AT+CRC?
+CRC: 0
OK
AT+CRC=1
OK
+CRING: VOICE
GPRS COMMANDS:
Command Description
AT+CGATT ATTACH/DETACH FROM GPRS SERVICE
AT+CGDCONT DEFINE PDP CONTEXT
AT+CGQMIN QUALITY OF SERVICE PROFILE (MINIMUM ACCEPTABLE)
AT+CGQREQ QUALITY OF SERVICE PROFILE (REQUESTED)
AT+CGACT PDP CONTEXT ACTIVATE OR DEACTIVATE
AT+CGDATA ENTER DATA STATE
AT+CGPADDR SHOW PDP ADDRESS
AT+CGCLASS GPRS MOBILE STATION CLASS
AT+CGEREP CONTROL UNSOLICITED GPRS EVENT REPORTING
AT+CGREG NETWORK REGISTRATION STATUS
AT+CGSMS SELECT SERVICE FOR MO SMS MESSAGES
AT+CGCOUNT GPRS PACKET COUNTERS
GSM Sim900A with Arduino:
Following are some of the projects which explain GSM Sim900A interfacing with Arduino and GSM Sim900A Arduino Code.
Following are the detailed GSM Sim900A-based projects.
Arduino Fire Alarm System with GSM Alert Text Message & Buzzer
Flood Monitoring System with SMS Alert using Arduino and GSM
Door Lock System using Arduino and GSM, Wireless Electronic Lock
Door Opening GSM alarm Wireless home security system using Arduino
How to use GSM and Bluetooth Together To monitor Any Sensors wirelessly using Arduino
RFID & GSM based student Attendance Alert message to parents
Arduino GSM Project: Security Alert message to multiple numbers
Request Temperature Data Using GSM and Arduino
Arduino and Gsm based laser security system